SARA-G450 - System integration manual
UBX-18046432 - R08
Design-in
Page 107 of 143
C1-Public
2.7
Audio interfaces
2.7.1
Analog audio interface
☞
The analog audio interface is not supported by the “00” product version. This interface should be
left unconnected and should not be driven by external devices.
2.7.1.1
Guidelines for microphone and speaker connection circuit design
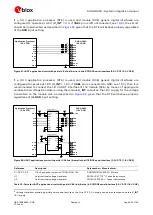
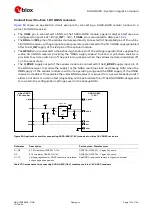
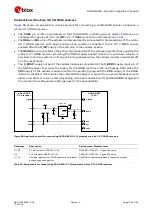
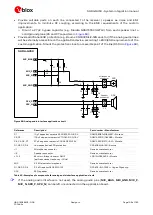
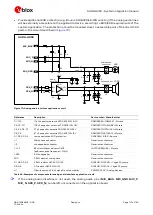
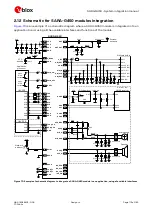
SARA-G450 modules provide one analog audio input path and one analog audio output path.
shows an application circuit for the analog audio interface, connecting a 2.2 k
Ω
electret
microphone and a 32
Ω
receiver / speaker:
External microphone can be connected to the uplink path of the module, since the module provides
supply and reference as well as differential signal input for the external microphone.
A 32
Ω
receiver / speaker can be directly connected to the balanced output of the module, since
the differential analog audio output of the module is able to directly drive loads with such a
resistance rating.
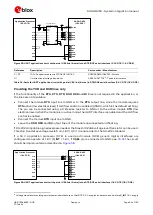
As in the example circuit in
, follow the general guidelines for the design of an analog audio
circuit:
Provide an appropriate supply to the used electret microphone, providing a clean connection from
the MIC_BIAS supply output to the microphone. It is suggested to implement a bridge structure:
o
The electret microphone, with its nominal intrinsic resistance value, represents one resistor of
the bridge.
o
To achieve good supply noise rejection, the ratio of the two resistances in one leg (R2/R3)
should be equal to the ratio of the two resistances in the other leg (R4/MIC), i.e. R2 must be
equal to R4 (e.g. 2.2 k
Ω
) and R3 must be equal to the microphone nominal intrinsic resistance
value (e.g. 2.2 k
Ω
).
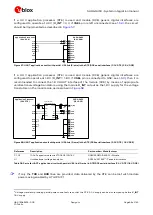
Provide an appropriate series resistor at the MIC_BIAS supply output and then mount a
corresponding large bypass capacitor to provide additional supply noise filtering. See the R1 series
resistor (2.2 k
Ω
) and the C1 bypass capacitor (10
µ
F).
Do not place a bypass capacitor directly at the MIC_BIAS supply output, since an appropriate
internal bypass capacitor is already provided to guarantee stable operation of the internal
regulator.
Connect the reference of the microphone circuit to the MIC_GND pin of the module as a sense line.
Provide an appropriate series capacitor at both MIC_P and MIC_N analog uplink inputs for DC
blocking (as the C2 and C3 100 nF Murata GRM155R71C104K capacitors in
). This
provides a high-pass filter for the microphone DC bias with a corresponding cut-off frequency
according to the value of the resistors of the microphone supply circuit. Then connect the signal
lines to the microphone.
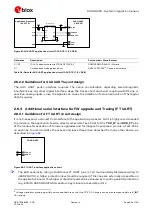
Provide suitable parts on each line connected to the external microphone as noise and EMI
improvements, in order to minimize RF coupling and TDMA noise, according to the custom
application requirements:
o
Mount an 82 nH series inductor with a Self-Resonance Frequency ~1 GHz (e.g. the Murata
LQG15HS82NJ02) on each microphone line (L1 and L2 inductors in
o
Mount a 27 pF bypass capacitor (e.g. Murata GRM1555C1H270J) from each microphone line to
solid ground plane (C4 and C5 capacitors in
Use a microphone designed for GSM applications, which typically has an internal built-in bypass
capacitor.
Connect the SPK_P and SPK_N analog downlink outputs directly to the receiver / speaker.