WCL488 Series Water Cooled Electronic Loads
Operation & Programming Manual
TDI-Dynaload Division
Page 90
402828, Rev. B1
40
28
25
-0
2-
19
.C
D
R
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
Le
ga
cy
S
ta
tu
s
Lo
gi
c
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
O
R
S
R
Q
Li
ne
S
R
Q
E
na
bl
e
M
as
k
S
R
Q
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
S
ys
te
m
M
aj
or
S
ys
te
m
M
in
or
M
aj
or
Fa
ul
t
M
in
or
Fa
ul
t
C
om
m
an
d
E
rr
or
S
in
gl
e
S
ho
t
C
om
pl
et
e
C
ha
ng
e
in
S
ta
tu
s
R
es
er
ve
d
S
ys
te
m
S
ta
tu
s
R
eg
is
te
r
S
TA
O
R
O
R
U
V
O
V
O
T
R
es
er
ve
d
O
C
O
P
S
AT
M
O
D
S
ys
te
m
M
aj
or
S
ys
te
m
M
in
or
M
aj
or
Fa
ul
t
M
in
or
Fa
ul
t
C
om
m
an
d
E
rr
or
S
in
gl
e
S
ho
t
C
om
pl
et
e
C
ha
ng
e
in
S
ta
tu
s
R
es
er
ve
d
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
U
V
O
V
O
T
G
P
IB
O
C
O
P
S
AT
M
O
D
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
U
V
1
1
G
P
IB
O
C
O
P
S
AT
M
O
D
Fa
ul
t S
hu
td
ow
n
M
as
k
co
nt
ro
ls
w
hi
ch
b
its
in
C
O
N
ca
us
e
a
sh
ot
do
w
n
S
D
N
La
tc
he
d
Fa
ul
t M
as
k
co
nt
ro
ls
w
hi
ch
C
O
N
bi
ts
g
et
la
tc
he
d
LA
T
Lo
ad
C
on
di
tio
n
R
eg
is
te
r
C
O
N
S
um
m
ar
y
B
it
E
na
bl
e
R
eg
is
te
r
S
B
E
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
R
es
er
ve
d
R
es
er
ve
d
R
es
er
ve
d
N
ot
A
llo
w
ed
To
o
Lo
ng
N
um
er
ic
R
an
ge
U
nr
ec
og
ni
ze
d
E
rr
or
C
om
m
an
d
R
eg
is
te
r
E
R
R
O
R
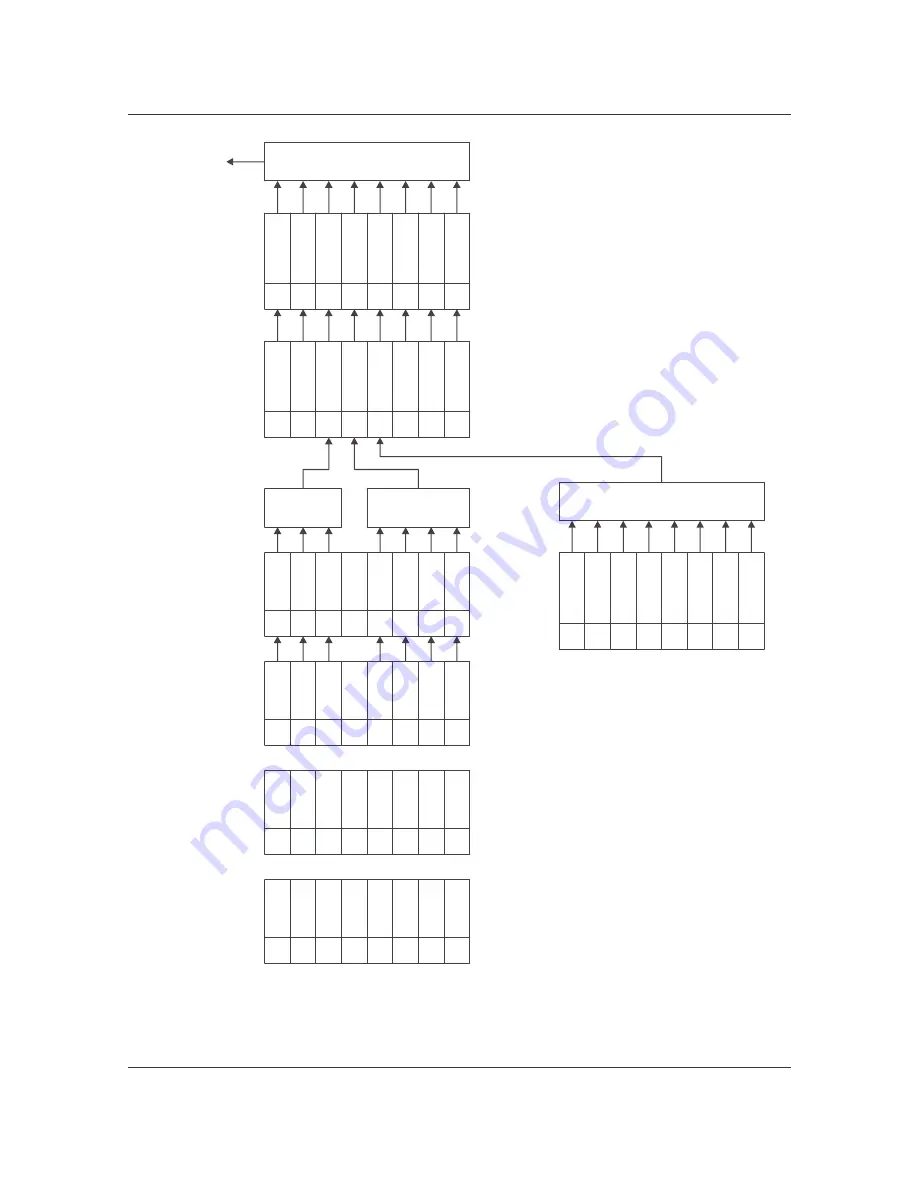
Figure 25. Load Status Structure