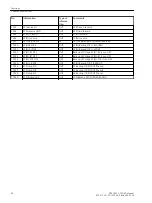
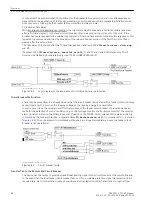
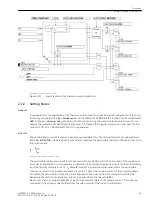
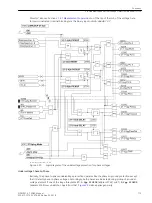
is connected. The possible initiation conditions for the breaker failure protection are those discussed above.
Depending on the application of the feeder protection, common phase or phase-segregated initiation condi-
tions may occur. Tripping by the breaker failure protection is always 3-pole.
T2 is used as time delay.
With two-element breaker failure protection, the trip command of the feeder protection is usually repeated,
after a first time element, to the feeder circuit breaker, often via a second trip coil or set of trip coils, if the
breaker has not responded to the original trip command. A second time element monitors the response to this
repeated trip command and trips the breakers of the relevant bus-bar section, if the fault has not yet been
cleared after this second time.
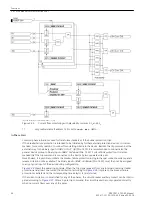
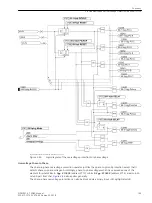
The time delay T2 is started after the T1 timer has expired if address 3913
T2StartCriteria
=
With exp.
of T1
.
If address 3913
T2StartCriteria
=
Parallel withT1
, T1 and T2 are started simultaneously. The T2
timer can be started by a separate binary input 1424
>50BFSTRTonlyT2
.
[lo-svs-2stufig-20101112, 1, en_US]
Figure 2-39
Logic diagram of the two-element circuit-breaker failure protection
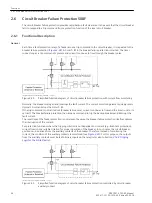
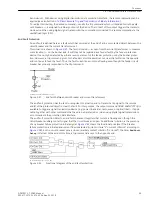
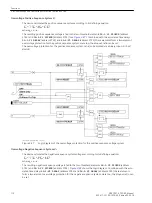
Circuit-Breaker Malfunction
There may be cases when it is already obvious that the circuit breaker associated with a feeder protection relay
cannot clear a fault, e.g. when the tripping voltage or the tripping energy is not available.
In such a case it is not necessary to wait for the response of the feeder circuit breaker. If provision has been
made for the detection of such a condition (e.g. control voltage monitor or air pressure monitor), the monitor
alarm signal can be fed to the binary input
>52 faulty
of the 7SD80. On occurrence of this alarm and a trip
command by the feeder protection, a separate timer
T3-BkrDefective
, which is normally set to 0, is started
(
). Thus, the adjacent circuit breakers (bus-bar) are tripped immediately in case the feeder circuit
breaker is not operational.
[logik-ls-gestoert-wlk-010802, 1, en_US]
Figure 2-40
Circuit-breaker faulty
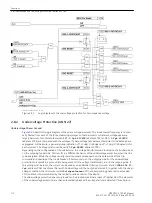
Transfer Trip to the Remote End Circuit Breaker
The device has the facility to provide an additional intertrip signal to the circuit breaker at the remote line end
in the event that the local feeder circuit breaker fails. For this, a suitable protection signal transmission link is
required (e.g. via communication cable, power line carrier transmission, radio transmission, or optical fiber
Functions
2.6 Circuit Breaker Failure Protection 50BF
98
SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018
Summary of Contents for SIPROTEC 4 7SD80
Page 8: ...8 SIPROTEC 4 7SD80 Manual E50417 G1100 C474 A2 Edition 02 2018 ...
Page 10: ...10 SIPROTEC 4 7SD80 Manual E50417 G1100 C474 A2 Edition 02 2018 ...
Page 18: ...18 SIPROTEC 4 7SD80 Manual E50417 G1100 C474 A2 Edition 02 2018 ...
Page 248: ...248 SIPROTEC 4 7SD80 Manual E50417 G1100 C474 A2 Edition 02 2018 ...
Page 298: ...298 SIPROTEC 4 7SD80 Manual E50417 G1100 C474 A2 Edition 02 2018 ...
Page 312: ...312 SIPROTEC 4 7SD80 Manual E50417 G1100 C474 A2 Edition 02 2018 ...
Page 322: ...322 SIPROTEC 4 7SD80 Manual E50417 G1100 C474 A2 Edition 02 2018 ...
Page 400: ...400 SIPROTEC 4 7SD80 Manual E50417 G1100 C474 A2 Edition 02 2018 ...
Page 402: ...402 SIPROTEC 4 7SD80 Manual E50417 G1100 C474 A2 Edition 02 2018 ...