Overview of Fail-safe Systems
1.3 Fail-safe Systems in SIMATIC S7
Safety Engineering in SIMATIC S7
1-8
System Manual, 04/2006, A5E00109529-05
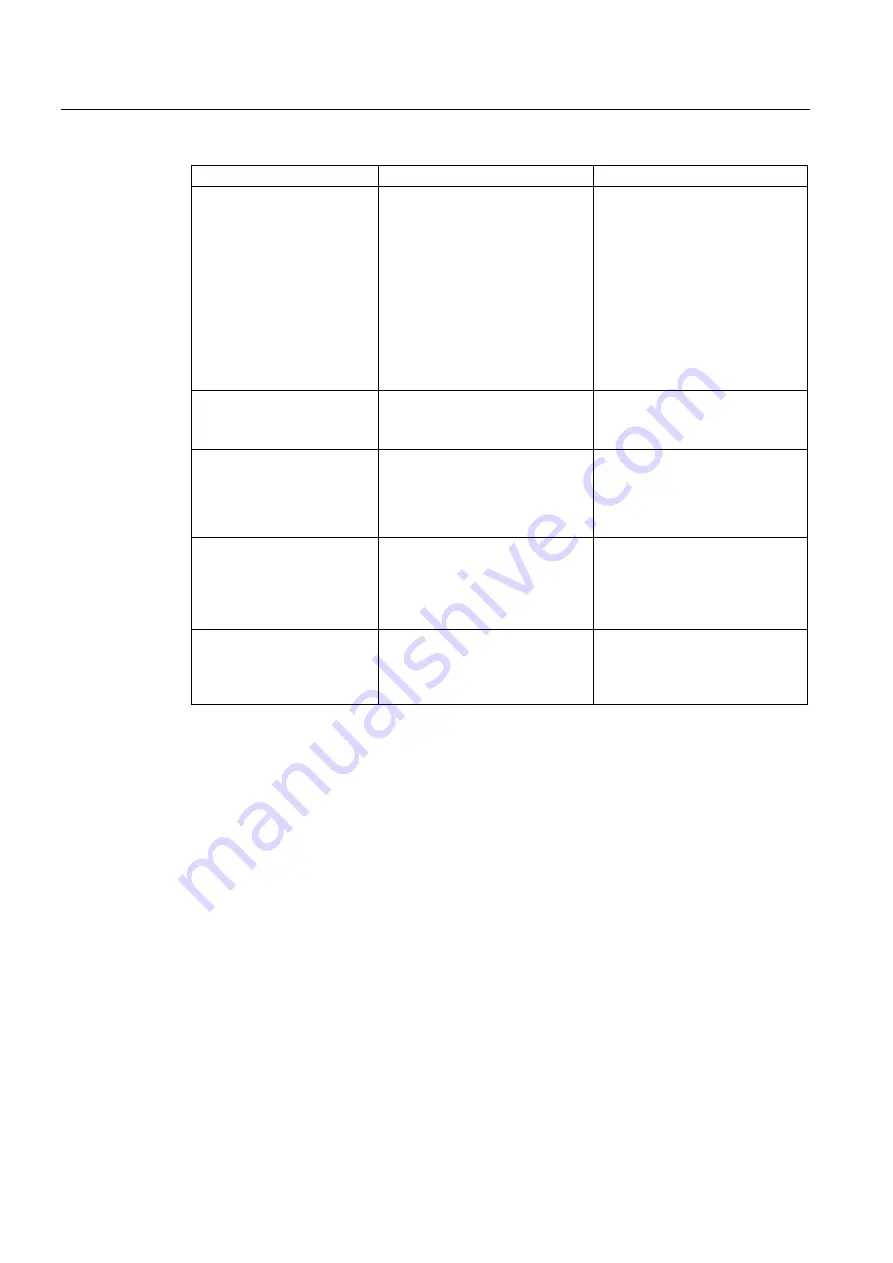
Performance Characteristic
S7 Distributed Safety
S7 F/FH Systems
Communication
Safety-related master-master
communication
Safety-related master-I-slave
communication
Safety-related I-slave-I-slave
communication
Safety-related I-slave-slave
communication
Safety-related communication via
S7 connections (Industrial
Ethernet only)
Safety-related communication via
S7 connections (via PROFIBUS,
MPI, Industrial Ethernet, etc.)
Creation of safety program
In standard LAD or FBD
languages in
STEP 7
In CFC (optional software for
STEP 7
)
via safety matrix
Modification of safety
program in the F-CPU in
RUN mode
Currently possible in deactivated
safety mode, however, transition
to safety mode possible only by
switching the F-CPU to STOP
mode
Currently possible in deactivated
safety mode or via Safety Data
Write; change of operating mode
of F-CPU not required for
transition to safety mode
Fault reactions in the safety
program
Passivation of channels or F-I/O
F-CPU in STOP mode
Passivation of channels or F-I/O
F-CPU does not go to STOP
mode; instead, the safety
program or faulty F-runtime group
is shut down
Main areas of application
Operator and machine protection
Burner control
Instrumentation and control and
process industries
(can be integrated in the
PCS 7 process control system)















































