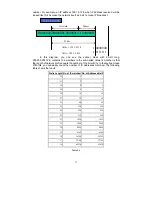
32
3-1-2. Account Configuration
In this function, only administrator can create, modify or delete the username
and password. Administrator can modify other guest identities’ password without
confirming the password but it is necessary to modify the administrator-equivalent
identity. Guest-equivalent identity can modify his password only. Please note that
you must confirm administrator/guest identity in the field of Authorization in advance
before configuring the username and password. Only one administrator is allowed
to exist and unable to be deleted. In addition, up to 4 guest accounts can be created.
The default setting for user account is:
Username : admin
Password : admin
Fig. 3-5
3-1-3. Time Configuration
The switch provides manual and automatic ways to set the system time via
NTP. Manual setting is simple and you just input “Year”, “Month”, “Day”, “Hour”,
“Minute” and “Second” within the valid value range indicated in each item. If you
input an invalid value, for example, 61 in minute, the switch will clamp the figure to
59.
NTP is a well-known protocol used to synchronize the clock of the switch
system time over a network. NTP, an internet draft standard formalized in RFC 1305,
has been adopted on the system is version 3 protocol. The switch provides four
built-in NTP server IP addresses resided in the Internet and an user-defined NTP
server IP address. The time zone is Greenwich-centered which uses the expression
form of GMT+/- xx hours.
Function name:
Time
Function description:
Set the system time by manual input or set it by syncing from Time servers.
The function also supports daylight saving for different area’s time adjustment.
Parameter description:
Current Time:
Show the current time of the system.
Summary of Contents for GS-2224L
Page 1: ......
Page 2: ......
Page 34: ...24 Fig 2 15 Office Network Connection Fig 2 14 Peer to peer Network Connection ...
Page 78: ...68 Fig 3 28 ...
Page 83: ...73 Fig 3 31 ...
Page 91: ...81 Fig 3 39 Fig 3 40 Fig 3 41 ...
Page 113: ...103 Fig 3 67 Ingress Port Fig 3 68 ...
Page 115: ...105 Fig 3 71 Fig 3 72 Fig 3 73 ARP Fig 3 74 ARP ...
Page 116: ...106 Fig 3 75 ARP Fig 3 76 ARP Fig 3 77 ARP Fig 3 78 ARP ...
Page 117: ...107 Fig 3 79 ARP Fig 3 80 ARP Fig 3 81 ARP Fig 3 82 ARP ...
Page 118: ...108 Fig 3 83 ARP Fig 3 84 ARP Fig 3 85 ARP Fig 3 86 ARP Fig 3 87 ARP ...
Page 119: ...109 Fig 3 88 IPv4 Fig 3 89 IPv4 Fig 3 90 IPv4 ...
Page 120: ...110 Fig 3 91 IPv4 Fig 3 92 IPv4 Fig 3 93 IPv4 Fig 3 94 IPv4 Fig 3 95 IPv4 ...
Page 121: ...111 Fig 3 96 IPv4 Fig 3 97 IPv4 Fig 3 98 IPv4 Fig 3 99 IPv4 Fig 3 100 IPv4 ...
Page 122: ...112 Fig 3 101 IPv4 Fig 3 102 IPv4 Fig 3 103 IPv4 Fig 3 104 IPv4 ...
Page 123: ...113 Fig 3 105 IPv4 Fig 3 106 IPv4 Fig 3 107 IPv4 ...
Page 124: ...114 Fig 3 108 IPv4 Fig 3 109 IPv4 Fig 3 110 IPv4 Fig 3 111 IPv4 ...
Page 125: ...115 Fig 3 112 IPv4 Fig 3 113 IPv4 Fig 3 114 IPv4 ...
Page 126: ...116 Fig 3 115 IPv4 Fig 3 116 IPv4 Fig 3 117 IPv4 ...
Page 127: ...117 Fig 3 118 Action Fig 3 119 Rate Limiter ...
Page 128: ...118 Fig 3 120 Port Copy Fig 3 121 DMAC Filter ...
Page 129: ...119 Fig 3 122 VLAN ID Filter Fig 3 123 VLAN ID Filter Fig 3 124 Tag Priority ...
Page 141: ...131 Fig 3 126 Set up Policy Rules Fig 3 127 Set up Policy Rules Fig 3 128 Set up Policy Rules ...
Page 143: ...133 Fig 3 132 Set up Port Policies Fig 3 133 Set up Port Policies Finish ...
Page 159: ...149 Fig 3 145 ...
Page 204: ...194 Fig 4 1 Fig 4 2 ...