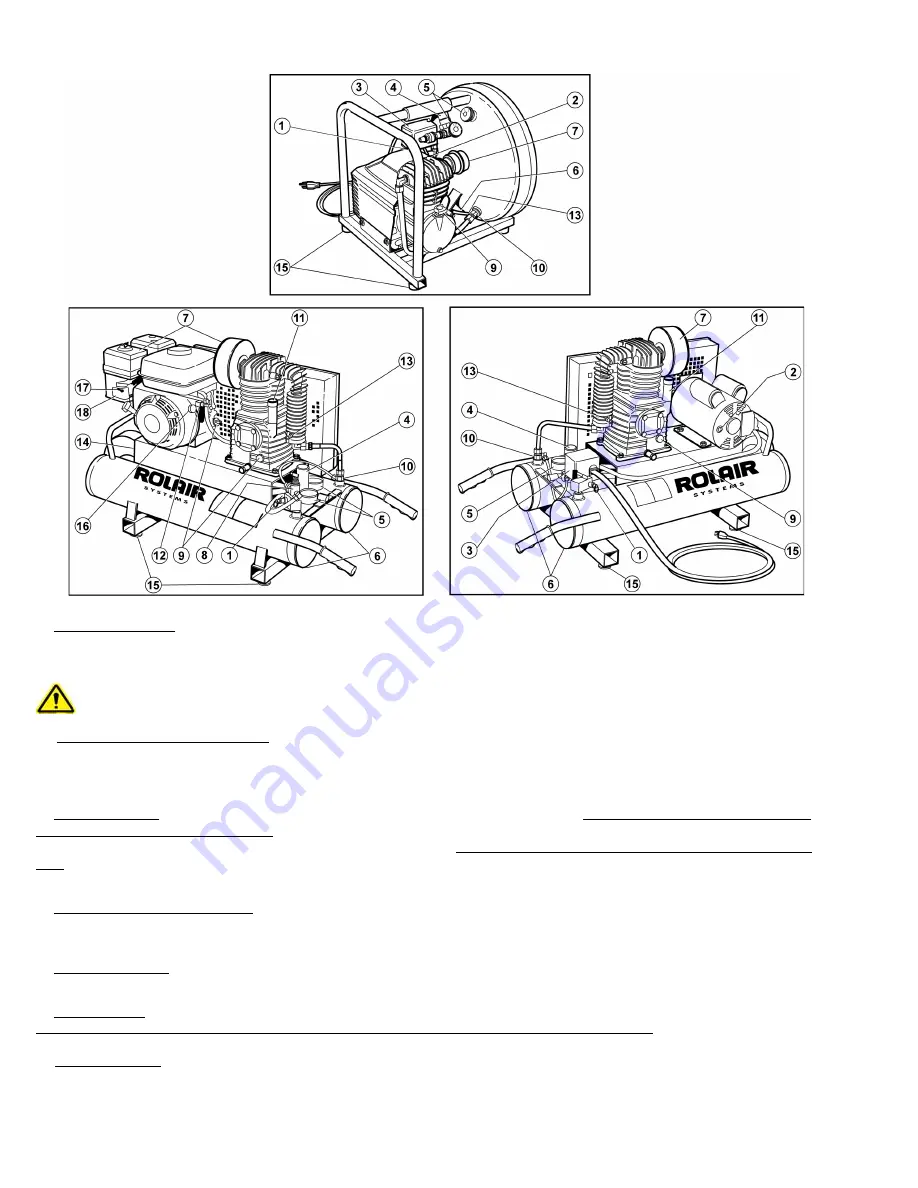
- 8 -
SYSTEM CONTROLS
(1) SAFETY-RELIEF VALVE
Every ROLAIR air compressor is equipped with a safety-relief valve which is designed to discharge tank pressure at a
predetermined setting when a systems failure occurs. Check the safety valve daily by pulling on the ring only when the tank pressure is
completely drained. The spring loaded valve should move freely within the safety valve body. An inoperable safety valve could allow an excessive
amount of tank pressure to build causing the air tank to violently rupture or explode.
Do not tamper with or attempt to eliminate the safety relief valve.
(2) MANUAL OVERLOAD / MOTOR RESET
Every ROLAIR
electric air compressor is built with manual overload protection. If the motor overheats,
the overload sensor will
trip
the reset button to protect the motor. If this occurs, please allow the motor to cool for approximately five minutes.
Locate and push in the reset button. The use of an undersized or excessive length of extension cord may be the cause of overheating. Re-
evaluate the power source and gauge/length of extension cord being used. (Refer to chart on page 10)
(3) PRESSURE SWITCH
Most electric air compressors are operated by the use of a pressure switch. Always make sure the lever is in the “Off”
position before plugging in the power cord. By moving the lever to the “On/Auto” position, the compressor will start and stop automatically
within the settings of the pressure switch which are typically 105 – 130 PSI. Do not attempt to stop the compressor by unplugging the power
cord. To stop, simply move the lever to the “Off” position. The lever operates a relief valve that dumps off head pressure and allows the
compressor to restart without load the next time it is used.
(4) REGULATOR – WORKING PRESSURE
To adjust the output/line pressure, simply lift up on the regulator adjustment knob and rotate clockwise
to increase working pressure or counterclockwise to decrease. Push adjustment knob back down to lock in setting. Never exceed the
manufacturer’s maximum allowable pressure rating of the tool being used or item being inflated.
(5) PRESSURE GAUGE(S)
Typically, most compressors are designed with a gauge to measure tank or storage pressure and another gauge attached
to the regulator that indicates output or working pressure.
(6) DRAIN VALVE(S)
One or more drain valves are installed to allow moisture to be drained on a daily basis from the compressor storage tank(s).
Open drains carefully and slowly to prevent scale, rust, or debris from becoming expelled at a high rate of speed.
(7) AIR INTAKE FILTER
Air intake filters are installed to prevent foreign matter from entering the engine or compressor pump. Check intake
elements on a regular basis and either clean or replace as needed. Warm soapy water or low compressed air may be used to clean the elements.
Check intake canisters or elbow components for cracks or broken seals and replace if structural problems are found.










































