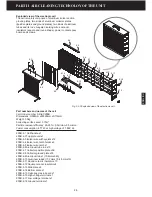
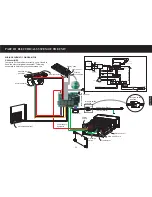
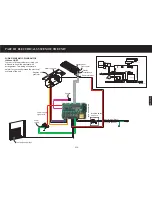
PART I GENERAL DESCRIPTION ON AIR CLEANING
ENGLISH
OZONE LEVELS AND THEIR EFFECTS
Data from IOA
Edited by Den (Zdenek) Rasplicka - Ozone Services
ppm = Parts per million volume air concentration
0.001 ppm
Lowest value detectable by hypersensitive humans. Too low to measure accurately with elaborate electronic equipment.
0.003 ppm
Threshold of odor perception in laboratory environment, 50 per cent confidence level.
0.003 ppm~0.010 ppm
The threshold of odor perception by the average person in clean air. Readily detectable by most normal persons. These
concentrations can be measured with fair accuracy. Ozone levels measured in typical residences and offices equipped with a
properly operating electronic air cleaner when outdoor ozone level is low. Infiltrating outdoor ozone could cause higher indoor
concentrations.
0.020 ppm
Threshold of odor perception in laboratory environment, 90 per cent confidence level.
0.00~0.125 ppm
Typical ozone concentrations found in the natural atmosphere. These levels of concentration vary with altitude, atmospheric
conditions and locale.
0.020~0.040 ppm
Representative average total oxidant concentrations in some major cities in 1964. Approximately 95 per cent or greater of these
oxidants are generally accepted to be ozone.
0.040 ppm
CSA limit for devices for household use. Measured as sustained concentration in test room.
0.050 ppm
Maximum allowable ozone concentration recommended by ASHRAE in an air conditioned and ventilated space.
Maximum allowable ozone concentration produced by electronic air cleaners and similar residential devices according to the
proposed amendment of the Federal Food, Drug and Cosmetic Act. (Note: Keep this figure in mind when selecting an ozone type
air purifier)
0.100 ppm
The maximum allowable ozone concentration in industrial working areas: permissible human exposure - 8 hours per day, 6 days a
week.
Continuous maximum ozone concentration allowable (per U.S. Navy_ in confined quarters such as atomic submarines).
Maximum allowable limit for industrial, public, or occupied spaces in England, Japan, France, the Netherlands and Germany.
0.15~0.51 ppm
Typical peak concentrations in American cities.
0.200 ppm
Prolonged exposure of humans under occupational and experimental conditions produced no apparent ill effects. The threshold
level at which nasal and throat irritation will result appears to be about 0.300 ppm.
0.300 ppm
The ozone level at which some sensitive species of plant life began to show signs of ozone effects.
0.500 ppm
The ozone level at which Los Angeles, California, declares its Smog Alert No. 1. Can cause nausea in some individuals. Extended
exposure could cause lung edema (an abnormal accumulation of serous fluid in connective tissue or serous cavity). Enhances the
susceptibility to respiratory infections.
1.00~2.00 ppm
Los Angeles, California, declares its Smog Alert No. 2 at 1.00 ppm ozone concentration and Smog Alert No. 3 at 1.500 ppm.
When this range of ozone concentration was inhaled by human volunteers for 2 hours, it caused symptoms which could be
tolerated without incapacitation with the symptoms subsiding after a few days. The symptoms were headache, pain in the chest,
and dryness of the respiratory tract.
1.40~5.60 ppm
The pinto bean exposed to 1.4 to 5.0 ppm ozone concentrations for 70 minutes showed some signs of severe injury to mature
leaves.
5.00~25.00 ppm
Experimentation showed that a 3 hour exposure at 12 ppm was lethal for Guinea pigs. Welders who were exposed to 9 ppm
concentration plus other air pollutants developed pulmonary edema. Chest X-rays were normal in 2 to 3 weeks, but 9 months later
they still complained of fatigue and exertional dyspnea (labored respiration).
25.00 ppm and up
Ozone concentrations that are immediately hazardous to human life are unknown but on the basis of animal experimentation, and
exposure at 50 ppm concentration for 60 minutes would probably be fatal.
1-5
Summary of Contents for R200T
Page 69: ...ENGLISH NOTES ...