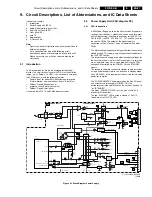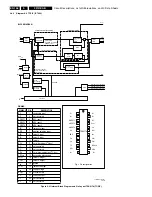
Circuit Descriptions, List of Abbreviations, and IC Data Sheets
EN 98
F21RE AB
9.
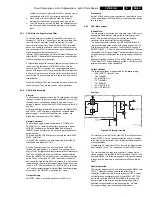
TS7600 blocks and so does TS7601. The voltage on pin 6 of
IC7611 increases in the same way as the 3V3.
If the 5V2 rises above 3V3, the 3V3 stabilizes and TS7600
starts to conduct. Capacitors C2656//C2690 are charged by
R3604 and R3605. At a voltage of 0.6 V, TS7601 will conduct
and the voltage at pin 6 of IC7611 becomes low again. The (P
is reset now.
If the PICNIC cannot communicate with the ROM, a reset is
generated by the watchdog. Pin 7 of the PICNIC generates a
pulse to create a new reset pulse for pin 6.
If one of the two supply voltages (3V3A, 3V3B) is absent, a
safety problem could occur. The 3V3A is the supply voltage for
the PICNIC and the 3V3B for the FALCONIC. If the 3V3 is too
low, the base of TS7601 will be low via TS7612 and TS7613. If
the base of TS7601 is made low, a RESET signal is generated
for the PICNIC.
9.4.5
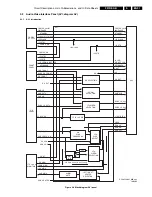
SSP: TOPIC and HOP (Diagram K6)
Introduction
The TOPIC (The most Outstanding Picture improvement IC,
item 7402, type TDA9178), is an (optional) IC between the
PICNIC and the HOP. It has the following (picture
improvement) functions:
•
Luminance Transient Processor (LTP), for detail
enhancement.
•
Chrominance delay circuitry, to compensate timing
differences between Y and C.
•
Spectral processor , for improved sharpness and colour
transient improvement (CTI).
•
Colour vector processor, for skin tone correction, green
enhancement and blue stretch.
•
Measure and detection circuitry, for AutoTV.
The sandcastle pulse from the HOP (High end Output
Processor), is fed to pin 1 of the TOPIC, which is used as
reference for timing.
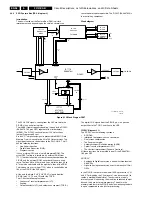
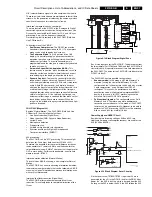
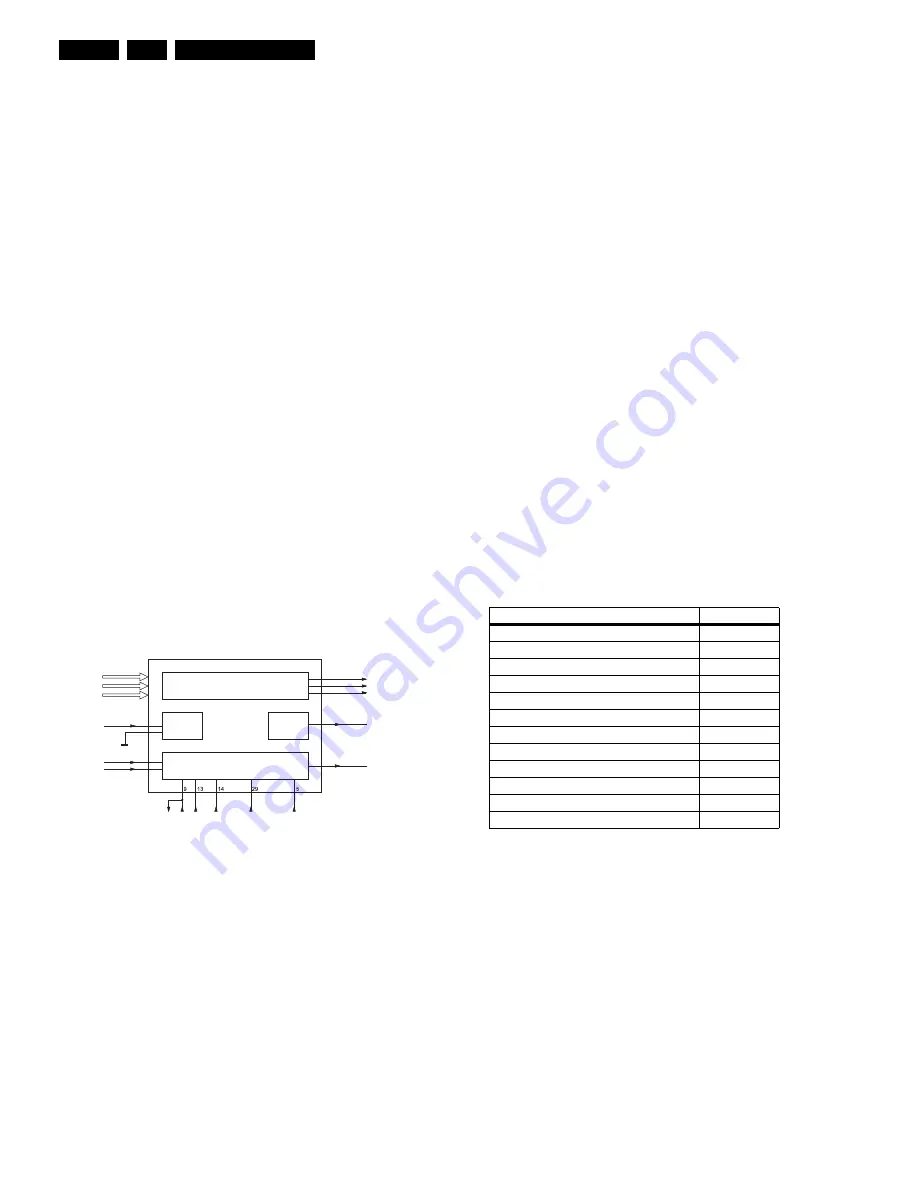
Figure 9-15 Block diagram HOP
The video processor and digital deflection processor are
integrated in the HOP (IC7300, TDA9330H). Its main functions
are:
•
RGB interface for OSD/CC.
•
Control of saturation, contrast, and brightness.
•
Black/blue stretch.
Operation
After input selection, the YUV input is converted to RGB
outputs. The RGB and fast blanking from the OTC (OSD and
CC) are inserted on pins 35 - 38.
Blue stretch, measures the amplitude of the three RGB signals.
If one of these colour signals reaches more than 80% of the
nominal value, the amplification of Red and Green decreases.
This is to achieve a higher colour temperature.
The RGB outputs are available at pins 40 - 42. They are
buffered and fed to connector 0340, which goes to the AV-
interface.
9.4.6
SSP: Audio processing
Introduction
The sound processing is distributed between the Flat Monitor
(amplifier) and the Receiver Box (processing). The sound
processing in the Receiver Box is completely done by the:
MSP 3410D: demodulation for Europe and AP (including
NICAM), or
MSP 3440G: demodulation for US/LatAm/Taiwan (this IC also
covers Korean stereo).
The MSP ICs contain audio processing, used for the basic L/R
stereo sound. This processing involves bass, treble (via the
equalizer), and balance (trim speakers). The volume is set to a
fixed value, because the volume control is done in the monitor
(via UART).
With the user interface, audio selection can be "mono",
"stereo", or "surround" mode (surround mode will give spatial
functionality). Stereo and spatial is only possible if a stereo
signal is available.
All the extra audio sources, compared with the SSP, can be
used in the main channel. The "Centre" input is available on the
AV-interface panel. With this input, it is possible to use the
monitor left and right speakers as a centre speaker in a home
cinema configuration. This input can be selected via the User
Interface.
For VGA it is not possible to select the "Centre" input, because
the E-box OSD is not working for VGA inputs.
The selection of the possible inputs is divided over two
separate panels: the SSP and the AVI panel. The input
configuration dependents on the E-box version (in combination
with a TEA6422 (item 7777), the MSP is also used for a part of
the source selection in the E-box).
Table 9-4 Audio I/O overview
9.5
Front Panel (FP, diagram FP)
9.5.1
General
This panel serves as an interface with the "outside world", and
has the following inputs/controls/indicators:
•
Power switch.
•
Power LED.
•
Audio L/R in.
•
Video CVBS in.
•
Video SVHS in.
•
Headphone out.
•
IR send-LED and receiver-LED (for Service).
•
IR receiver (for Remote Control).
•
Control buttons for MENU, PROGRAM, and VOLUME.
CL 16532023_053.eps
240901
VIDEO CONTROL
TDA 9330 AH
H O P
SUPPLY
DAC
GEOMETRY
IC 7300 / TDA9330H
Y, U, V FEAT
RGB PIP
RGB TXT
R
G
B
HOP DAC
LINE DRIVE
FBCSO
8V6
HD
VD
SC
1FH/2FH
VFB HFB
DYN
PHASE
CORR.
Audio inputs and outputs (EU/AP)
Location
RF input
SSP
EXT1= SCART1 L/R-in and L/R-out
SSP
EXT2= SCART2 L/R-in and L/R-out
SSP
EXT3= SCART3 L/R-in
SSP
EXT4= SCART4 L/R-in
SSP
SD L/R (YPbPr-1fH)
SD panel
VGA L/R-in
AVI panel
Center audio in
AVI panel
Front L/R-in
Front panel
VGA audio out for FTV monitor L/R-out
AVI panel
CL-out for a Dolby audio receiver
SSP
Headphone out L/R
Front panel
Summary of Contents for F21RE
Page 7: ...Directions for Use EN 7 F21RE AB 3 3 Directions for Use ...
Page 8: ...Directions for Use EN 8 F21RE AB 3 ...
Page 9: ...Directions for Use EN 9 F21RE AB 3 ...
Page 10: ...Directions for Use EN 10 F21RE AB 3 ...
Page 11: ...Directions for Use EN 11 F21RE AB 3 ...
Page 12: ...Directions for Use EN 12 F21RE AB 3 ...
Page 13: ...Directions for Use EN 13 F21RE AB 3 ...
Page 14: ...Directions for Use EN 14 F21RE AB 3 ...
Page 15: ...Directions for Use EN 15 F21RE AB 3 ...
Page 16: ...Directions for Use EN 16 F21RE AB 3 ...
Page 17: ...Directions for Use EN 17 F21RE AB 3 ...
Page 18: ...Directions for Use EN 18 F21RE AB 3 ...
Page 19: ...Directions for Use EN 19 F21RE AB 3 ...
Page 20: ...Directions for Use EN 20 F21RE AB 3 ...
Page 21: ...Directions for Use EN 21 F21RE AB 3 ...
Page 22: ...Directions for Use EN 22 F21RE AB 3 ...
Page 23: ...Directions for Use EN 23 F21RE AB 3 ...
Page 24: ...Directions for Use EN 24 F21RE AB 3 ...
Page 25: ......
Page 114: ...Revision List EN 114 F21RE AB 11 11 Revision List First release ...