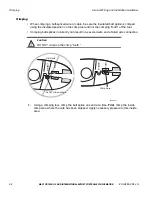
Data Satellite and GPS Network
How the MCP100 Works
1-4
MAY CONTAIN U.S. AND INTERNATIONAL EXPORT CONTROLLED INFORMATION
80-J4866-2 Rev. G
Data Satellite and GPS Network
Data Satellite
• Located approximately 22,300 miles over the equator at 83° west longitude (south of
Georgia).
• Uses Ku-band signals to handle all two-way information traffic between the vehicle and the
NMC.
• Offers ubiquitous coverage even in remote locations.
What Is the GPS Network?
• A worldwide radio-navigation system formed from a constellation of 24 satellites and their
ground stations.
• Uses satellites as reference points to calculate positions accurate to a matter of meters.
• A standard feature of the MCP100 for positioning.
• MCP100 receives positioning data from the GPS receiver, which is integrated inside the
antenna to determine location.
• Position data from the MCP100 is forwarded to dispatch whenever information is sent to a
vehicle and acknowledged, and whenever a driver sends information.
• Position data is sent at regular intervals and is made available to dispatch.
Code Division Multiple
Access (CDMA)
Wireless Network
• Radio frequency (RF) signals are received from the
antenna by the MCP100 via the terrestrial data modem
(TDM) from a wireless communication network, which
varies depending on geographic location.
Data Satellite
• Handles all two-way information traffic between the
vehicle and the NMC when using a satellite data modem
(SDM).
GPS Positioning Satellites
• Uses 24 satellites to provide vehicle positioning
information.
Mobile Computing Platform
(MCP100)
• Driver’s interface with the Omnitracs platform and the
component that resides in the vehicle.
• Allows the driver to send and receive information.