5.
From the Internet Connection Type menu, select 6rd Tunnel.
The page adjusts. The router automactially detects the information in the following sections:
•
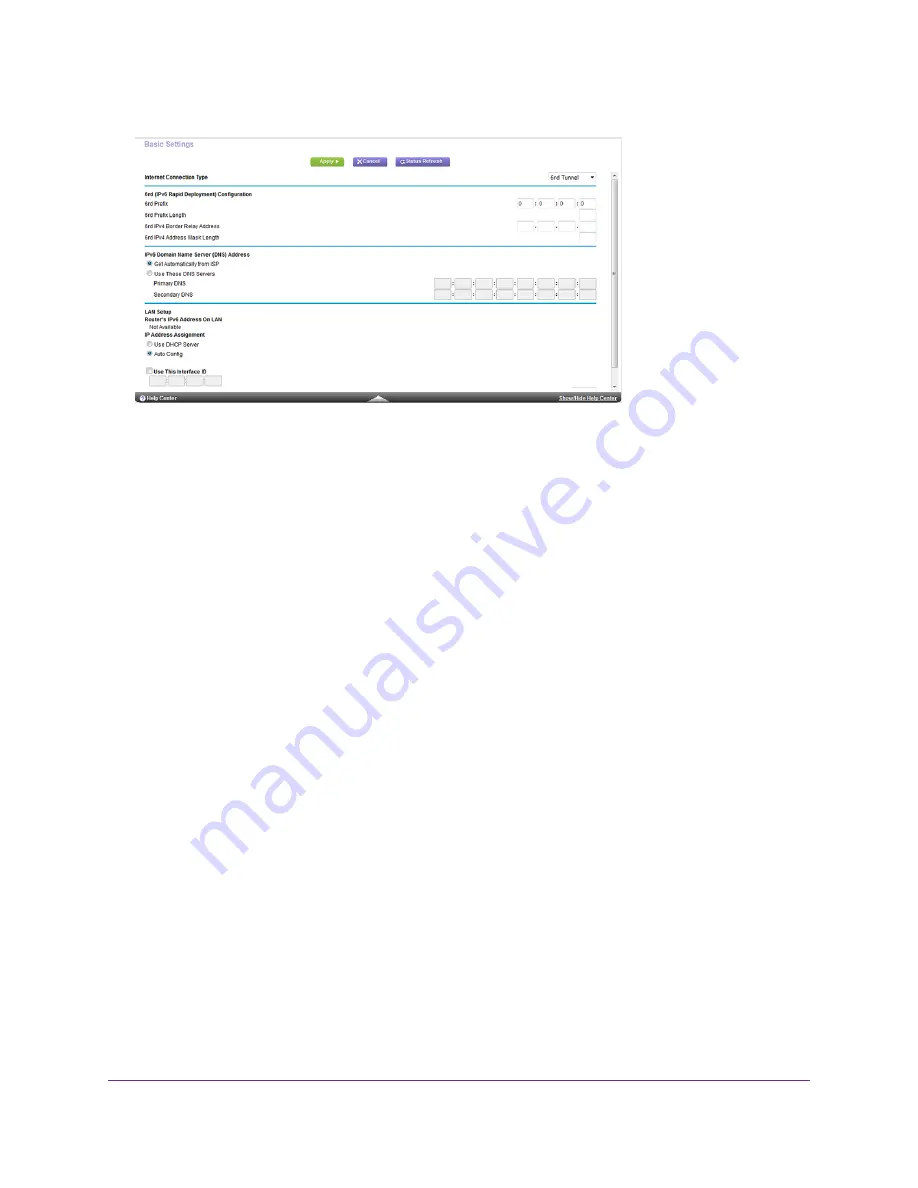
6rd (IPv6 Rapid Development) Configuration. The router detects the service provider’s IPv4 network and
attempts to establish an IPv6 6rd tunnel connection. If the IPv4 network returns 6rd parameters to the router,
the page adjusts to display the correct settings in this section.
•
Router's IPv6 Address on LAN. This field shows the IPv6 address that is acquired for the router’s LAN
interface. The number after the slash (/) is the length of the prefix, which is also indicated by the underline
(_) under the IPv6 address. If no address is acquired, the field displays Not Available.
•
MTU size (in bytes). The normal MTU (maximum transmit unit) value for most Ethernet networks is 1500
bytes, or 1492 bytes for PPPoE connections. Change the MTU only if you are sure that it is necessary for
your ISP connection. For more information about changing the MTU size, see
on page
43.
6.
Select an IPv6 Domain Name Server (DNS) Address radio button:
•
Get Automatically from ISP. Your ISP uses DHCP to assign your DNS servers. Your ISP automatically
assigns this address.
•
Use These DNS Servers. If you know that your ISP requires specific servers, select this option. Enter the
IP address of your ISP’s primary DNS server. If a secondary DNS server address is available, enter it also.
7.
Select an IP Address Assignment radio button:
•
Use DHCP Server. This method passes more information to LAN devices but some IPv6 systems might not
support the DHCPv6 client function.
•
Auto Config. This is the default setting.
This setting specifies how the router assigns IPv6 addresses to the devices on your home network (the LAN).
8.
(Optional) Select the Use This Interface ID check box and specify the interface ID that you want to be used for
the IPv6 address of the router’s LAN interface.
Specify Your Internet Settings
42
Nighthawk X8 AC5000 Tri-Band WiFi Router
















































