30
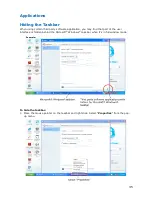
Tips for Using Windows
®
XP
This section provides various tips that should help you get the most of your Windows
®
XP
operating system.
Note
If you are familiar with previous versions of Microsoft
®
Windows
®
, we advise you to
check out the new features specific to Windows
®
XP operating system. To do so,
click on
Start
, click on
Help and Support
, and pick the
What's new in Windows
®
XP
topic.
Booting in Safe Mode
Safe mode helps you diagnose problems. If a symptom does not reappear when you start in
safe mode, you can eliminate the default settings and minimum device drivers as possible
causes. If a newly added device or a changed driver is causing problems, you can use the safe
mode to remove the device or reverse the change.
In safe mode, you have access to basic files and drivers only (i.e. mouse, monitor, keyboard,
mass storage, base video, default system services, and no network connections).
There are circumstances where safe mode will not be able to help you, such as when the
system files that are required to start the notebook are corrupted or damaged. If your
notebook does not start successfully using the safe mode, you might need to use either the
Windows
®
Recovery Console
feature (click on
Start
,
Help and Support
for more information),
or to restore your notebook using the
Recovery Program
(refer to the Quick Reference
delivered with your notebook).
Restarting in Safe Mode
1.
Click on
Start
,
Turn Off Computer
, and then click on
Restart
.
2.
When you see the message “
Please select the operating system to start”
, press
F8
.
3.
Use the arrow keys to highlight the appropriate safe mode option, and then press
Enter
.
•
Safe Mode
- starts your notebook using only the basic files and drivers (see above).
Use this mode to run the system tools, such as the Disk Defragmenter.
•
Safe Mode with Networking
- starts your notebook using only the basic files and
drivers (see above), and network connections.
•
Safe Mode with Command Prompt
- starts your notebook using only the basic files
and drivers (see above). After logging on, the command prompt is displayed instead of
the graphical user interface. You will be asked to choose a user, or to log on as
administrator. Depending on what you choose, the default directory of the command
prompt will be different.
•
Enable Boot Logging
- the notebook creates a log file (Ntbtlog.txt) that records the
loading of each service and device. The boot log is useful in determining the exact
cause of notebook start-up problems.
•
Enable VGA Mode
- starts Windows
®
using the basic VGA driver.
•
Last Known Good Configuration
- starts your notebook using the registry
information and drivers that was saved at the last shutdown. Any changes made since
the last successful start-up will be lost.