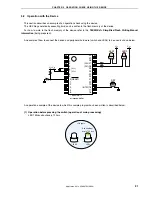
CHAPTER 3 SOFTWARE
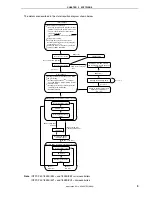
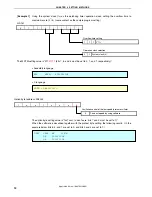
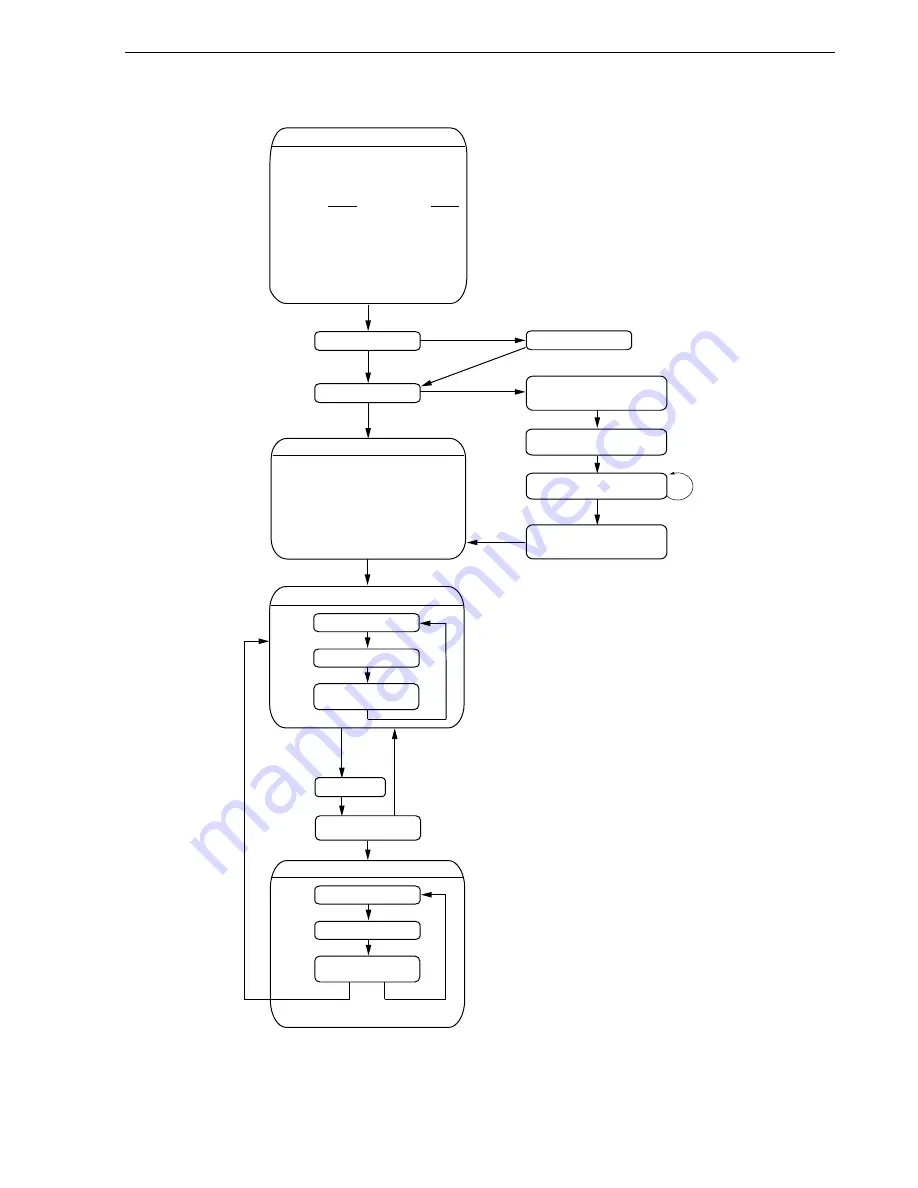
The details are described in the state transition diagram shown below.
Initial settings 1
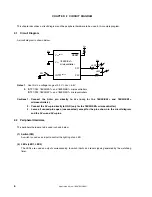
Referencing the option byte
• Selecting the high-speed internal oscillator
(8 MHz (TYP.)) as the system clock source
• The low-speed internal oscillator can be
stopped by software
• The P34/RESET pin is used as the RESET
pin
Stack pointer setting
Selecting the system clock (f
X
) for the
watchdog timer operation clock, setting the
overflow time to 2
20
/f
X
Setting the CPU clock frequency to 2 MHz
Turning off LED1 and LED2
Reset source check 1
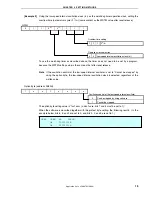
Initial settings 2
Setting the CPU clock frequency to 4 MHz
I/O port setting
• Setting only P43/INTP1
Note
as an input
port, and using an internal pull-up resistor
Interrupt setting
• Setting the valid edge of INTP1 (external
interrupt) to the falling edge
• Enabling interrupt
Setting V
LVI
to 2.85 V
±
0.15 V
and starting low-voltage detection
operation
Setting so that an internal reset
signal is generated when
V
DD
< V
LVI
V
DD
≥
V
LVI
Clearing the watchdog timer
WDT reset
LVI reset
Lighting LED2
Reset other than by WDT
Reset source check 2
POC reset or external
reset
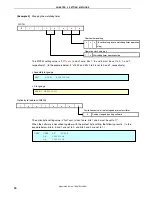
Blinking LED1 every 120 ms (main processing)
Blinking LED1 every 60 ms (interrupt servicing)
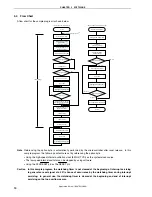
INTP1 =
Low level
INTP1 =
High level
10 ms wait
INTP1 falling edge
detection
INTP1 = High level
(chattering detection)
INTP1 = Low level
Clearing the INTP1
interrupt request
200 s wait
Reversing LED1 output
120 ms wait
Clearing the watchdog
timer
Reversing LED1 output
60 ms wait
Clearing the watchdog
timer
V
DD
<
V
LVI
•
•
•
•
•
μ
•
•
•
Note
INTP1/P43: 78K0S/KA1+ and 78K0S/KB1+ microcontrollers
INTP1/P32: 78K0S/KY1+ and 78K0S/KU1+ microcontrollers
Application Note U18847EJ1V0AN
9