© National Instruments
|
5-9
NI cDAQ-9132/9133/9134/9135/9136/9137 User Manual
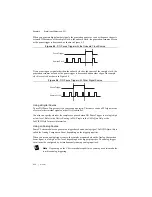
Sample Clocked Buffered Pulse Measurement
A sample clocked buffered pulse measurement is similar to single pulse measurement, but a
buffered pulse measurement takes measurements over multiple pulses correlated to a sample
clock.
The counter performs a pulse measurement on the Gate. On each sample clock edge, the counter
stores the high and low ticks in the FIFO of the last pulse to complete. The STC3 transfers the
sampled values to host memory using a high-speed data stream.
Figure 5-10 shows an example of a sample clocked buffered pulse measurement.
Figure 5-10.
Sample Clocked Buffered Pulse Measurement
Note
If a pulse does not occur between sample clocks, an overrun error occurs.
For information about connecting counter signals, refer to the
section.
Semi-Period Measurement
In semi-period measurements, the counter measures a semi-period on its Gate input signal after
the counter is armed. A semi-period is the time between any two consecutive edges on the Gate
input.
You can route an internal or external periodic clock signal (with a known period) to the Source
input of the counter. The counter counts the number of rising (or falling) edges occurring on the
Source input between two edges of the Gate signal.
You can calculate the semi-period of the Gate input by multiplying the period of the Source
signal by the number of edges returned by the counter.
Refer to the following sections for more information about semi-period measurement options:
•
Single Semi-Period Measurement
•
Implicit Buffered Semi-Period Measurement
Co
u
nter
Armed
G
a
te
S
o
u
rce
H L
2 2
H L
2 2
3 3
Sa
mple
Clock
S
1
S
2
B
u
ffer
2
2
3
3