Disk/Tape Controller Data
B-4
MVME166 Single Board Computer Installation Guide
B
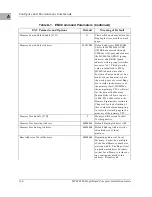
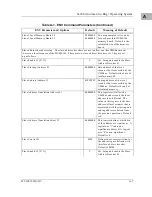
MVME328 -- 14 Devices
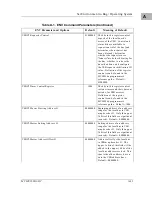
MVME350 -- 1 Device
Controller LUN
Address
Device LUN
Device Type
6
$FFFF9000
00
08
10
18
20
28
30
SCSI Common Command Set
(CCS), which may be any of these:
- Removable flexible direct access
(TEAC style)
- CD-ROM
- Sequential access
7
$FFFF9800
16
$FFFF4800
40
48
50
58
60
68
70
Same as above, but these
will only be available if
the daughter card for the
second SCSI channel is present.
17
$FFFF5800
18
$FFFF7000
19
$FFFF7800
Controller LUN
Address
Device LUN
Device Type
4
$FFFF5000
0
QIC-02 streaming tape drive
5
$FFFF5100
Summary of Contents for MVME166
Page 1: ...MVME166 Single Board Computer Installation Guide MVME166IG D2 ...
Page 12: ...xii ...
Page 14: ...xiv ...
Page 46: ...Hardware Preparation and Installation 2 10 MVME166 Single Board Computer Installation Guide 2 ...
Page 70: ...Debugger General Information 3 24 MVME166 Single Board Computer Installation Guide 3 ...
Page 114: ...Disk Tape Controller Data B 6 MVME166 Single Board Computer Installation Guide B ...
Page 116: ...Network Controller Data C 2 MVME166 Single Board Computer Installation Guide C ...