Positioning Control
Components of Positioning Control and Their Roles 3
3-6
3.1.5
Zero point return function
•
There are two types of servo motor encoders, incremental type (pulse count method) and
absolute type (absolute position detection method).
•
Incremental type is constructed so that the current value stored in the position controller
does not increase or decrease, even if the workpiece stop position changes by some
reason while the power is turned off, therefore the positioning address is not assured.
•
Accordingly, when the power is turned on, the machine should be moved to the reference
point to update the zero point address. This operation is called return to zero point.
•
Absolute type is constructed so that the current value stored in the position controller
increases or decreases if the workpiece stop position changes while the power is turned off,
thus the positioning address is assured. Accordingly, when the power is turned on, return to
the zero point is not required.
However, when the machine is used for the first time, it should be returned to the zero point
so that it recognizes the zero point address.
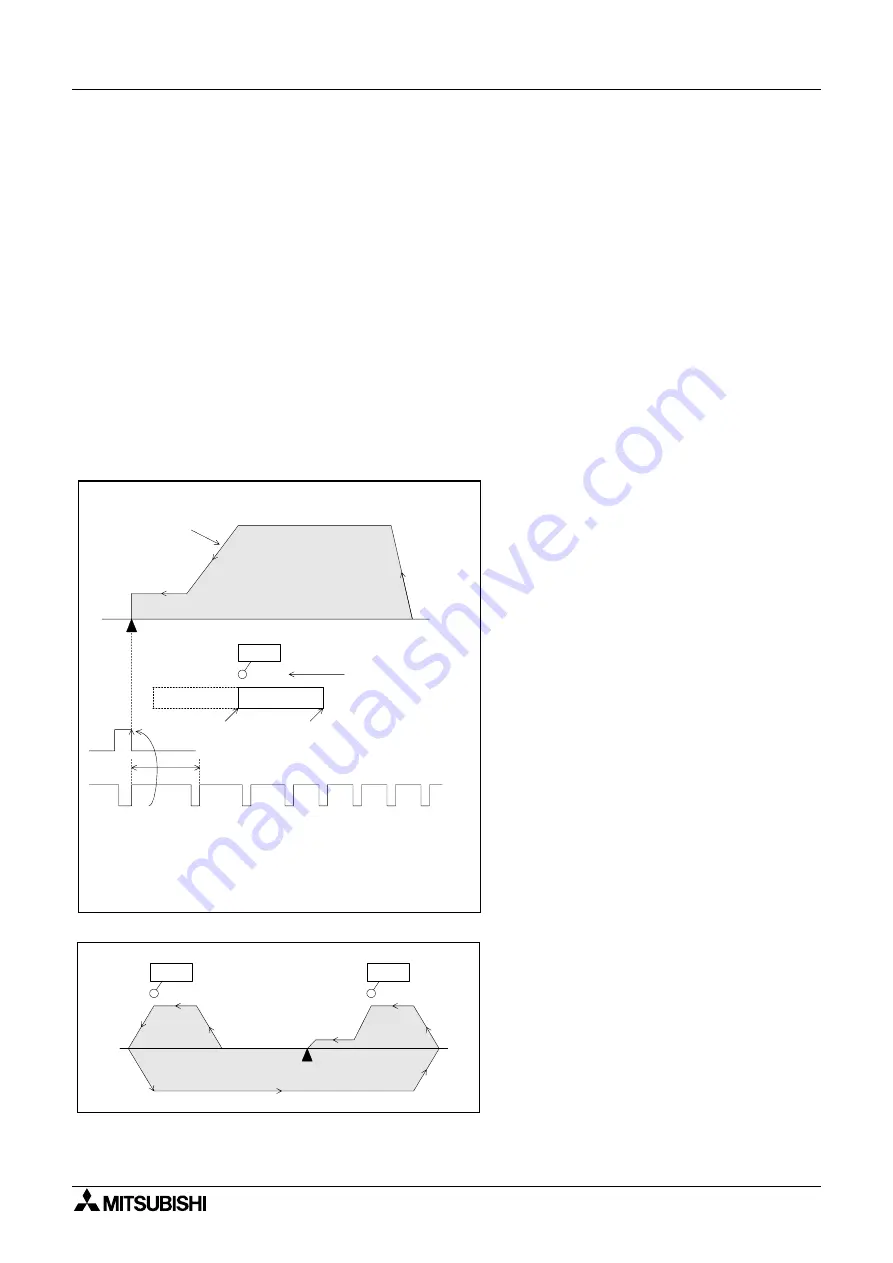
< Operation to return to the zero point >
• The zero point return direction, return
speed, deceleration time and creep speed
are set by parameters in the positioning
controller.
• There are several zero point return
methods.
For example, when the forward end of the
dog reaches the dog switch, the motor
resumes its creep speed. At the first zero
point signal after the dog reaches the
backward end, the deviation counter clear
signal is output and the motor stops.
• The zero point address set by a parameter
is written to the current value register of
the position controller.
• In some models, if the zero point return
operation is performed while the work
piece is stopped beyond the dog switch,
the machine moves once until the limit
switch is actuated, inverts the direction,
then returns to the zero point again (dog
search function, zero point return retry
function).
Dog
Dog
switch
Zero point
return direction
Zero point
return speed
Creep
speed
Initial position
Deceleration time
Dog
Backward end
Forward end
Zero point
Clear signal
*
The return point of the dog switch should be adjusted
to a midpoint of the zero point signal (1 pulse per
rotation of the motor).
In this example, the dog length should not be less than
the deceleration distance of the machine.
*
Limit
switch
Initial
position
Escape operation
Dog
switch
Zero point
Summary of Contents for MELSEC-F
Page 1: ...Positioning Control Training Manual ...
Page 4: ...Positioning Control ii ...
Page 6: ...Positioning Control iv ...
Page 8: ...Positioning Control vi ...
Page 10: ...Positioning Control Contents viii ...
Page 12: ......
Page 20: ......
Page 26: ......
Page 38: ...Positioning Control Components of Positioning Control and Their Roles 3 3 12 ...
Page 40: ......
Page 46: ...Positioning Control Advanced Positioning 4 4 6 ...
Page 48: ......
Page 58: ......
Page 68: ......
















































