© 2017 Sensata Technologies
45
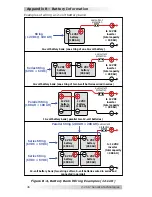
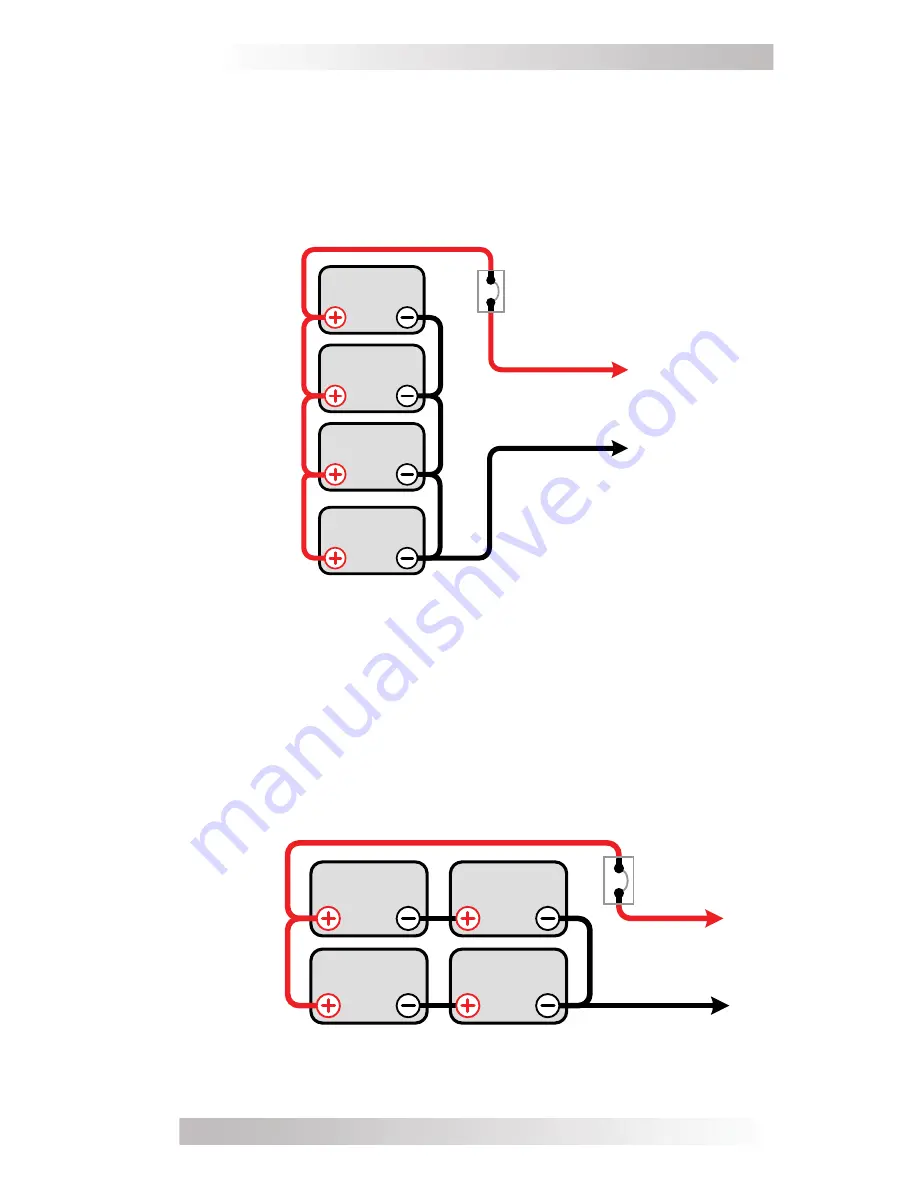
Figure B-3, Series-Parallel Battery Wiring
overcurrent
protection
String 2
String 1
12 volt battery bank (total capacity = 400 AHrs)
To
12 VDC
Inverter
6 volts
(200 AHrs)
6 volts
(200 AHrs)
6 volts
(200 AHrs)
6 volts
(200 AHrs)
(First)
(Last)
Series-Parallel Wiring
– A series-parallel con
fi
guration increases
both voltage (to match the inverter’s DC requirements) and capacity
(to increase run time for operating the loads) using smaller, lower-
voltage batteries. In the example below (Figure B-3), four 6 VDC/200
AHr batteries are combined into two strings resulting in a 12 VDC/400
AHr battery bank.
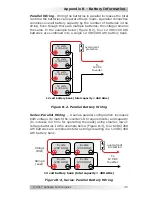
Figure B-2, Parallel Battery Wiring
12 volt battery bank (total capacity = 400 AHrs)
overcurrent
protection
12 volts
(100 AHrs)
12 volts
(100 AHrs)
12 volts
(100 AHrs)
12 volts
(100 AHrs)
To
12 VDC
Inverter
Parallel Wiring
– Wiring the batteries in parallel increases the total
run time the batteries can operate the AC loads. A parallel connection
combines overall battery capacity by the number of batteries in the
string. Even though there are multiple batteries, the voltage remains
the same. In the example below (Figure B-2), four 12 VDC/100 AHr
batteries are combined into a single 12 VDC/400 AHr battery bank.
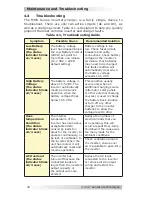
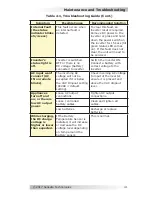
Appendix B – Battery Information