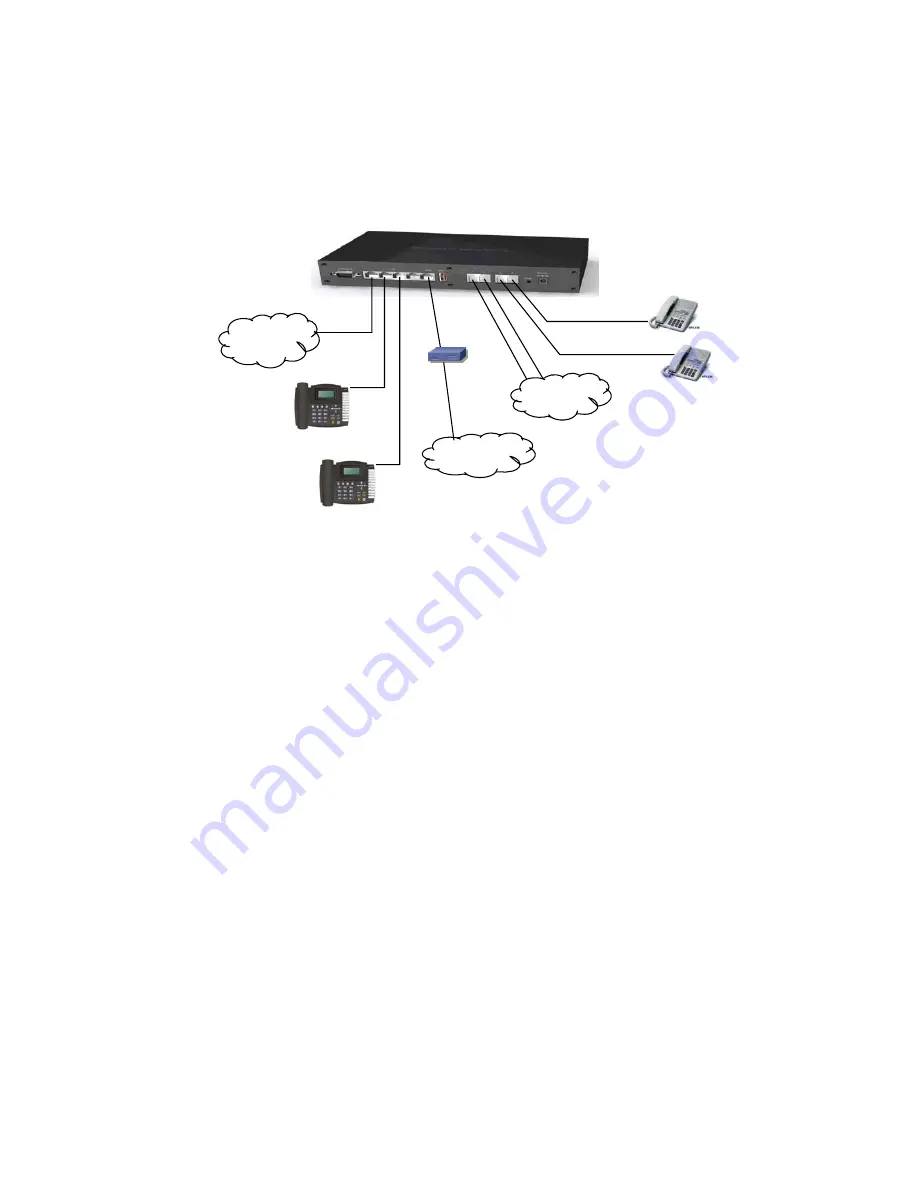
3.1. Case I: Single-Site IP PBX
This case shows typical settings of a single-site configuration for SMB Companys.
The IP PBX combines the telephony network and the data network with ADSL/Cable
modem connection to Internet access and 2 PSTN subscriber lines as shown in
Figure 5-1. The provisioning tasks include:
Figure 5-1 Single-Site IP PBX Network Connections
There are staff phones in cubes and offices and utility phones in public areas.
Staff and utility phones can be either IP phones or analog phones (POTS).
Each phone has one extension and it can call any extension without limitation.
Only staff phones can call out to PSTN with a prefix 9.
Incoming PSTN calls are answered by auto attendant and could be transferred to
any extension.
Configuration steps:
1. Create usergroups staff, utility, and ext-all.
2. Include staff and utility in the Reachable usergroup of ext-all.
3. Create a user account for each staff and assign it to usergroup staff.
4. Create an additional user account public and assign it to usergroup utility.
5. Create a device for each physical phone and designate an extension.
6. Assign extensions of staff phones to corresponding users.
7. Assign all extensions of utility phones to share the same user public.
8. Create a route pstn with pattern 9. with number of digits stripped 1, no prefix.
9. Create a routegroup pstn-out containing route pstn only.
10. Create a PSTN trunk with ID 1, port 1-2, choose pstn-out as Outbound routegroup, leave
DID unchecked, and select ext-all as the Usergroup of privilege.
11. Return to usergroup configuration. For usergroup staff, include PSTN trunk pstn1 and
Reachable usergroup utility; while for usergroup utility, include Reachable usergroup
staff only.
12. Reload IP PBX Service.
Internet
ADSL
modem
PSTN
IP Phones
POTS
FXS
FXO
Ethernet
LAN























