OSCILLATOR PARAMETERS (MAIN MODE) | 25
GLIDE (ON/OFF)
Sync allows you to synchronize the frequency of the oscil
-
lator to divisions of the MIDI clock signal. The range is from
1/128 of a beat, to 8 beats. No Track turns off keyboard
tracking, and allows you to specify the oscillators fixed
frequency from 0 Hz to 20 kHz. Low simply lowers the
frequency of the oscillator by 60 semitones, as a means to
quickly switch the oscillator into sub-audio rates.
Page 2 Parameters
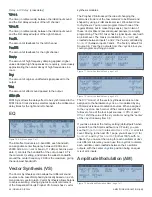
Figure 28. Oscillator Main Mode, page 2
Figure 28 shows page 2 of the
Main
mode controls for the
Multimode oscillator. The following section describes the
page 2 parameters at a high level. For a detailed descrip-
tion of the parameters and values available for each oscilla-
tor type, please refer to “Appendix 2- Modulation Sources”
on page 54.
Sync
This control can be used to synchronize the selected
oscillator to another oscillator, which causes the selected
oscillator (the slave) to restart its waveform every time the
master oscillator cycles its waveform. The pitch of the slave
oscillator is locked to that of the master oscillator, and the
Coarse and Fine frequency controls of the slave oscillator
affect only how many cycles the slave plays relative to the
master. Sweeping the frequency of the slave oscillator cre
-
ates the classic hard sync sound. Synchronizing the oscil-
lator to Gate causes the oscillator to restart with each note
on event. Note that an oscillator cannot be synchronized to
itself.
Phase
Phase
controls the start point of the waveform when it re-
ceives a sync’ed signal. If
Gate
is the sync source, adjust-
ing the
Phase
will allow you to force the oscillator to start
from that phase point for every time a key is pressed. (This
is the same as for the Rotor’s
Phase
control). This is useful
when you wish to guarantee that the phase of the oscillator
will always restart at the same place when working on cre-
ating kick drum sounds, for example; otherwise, repeated
note events would sound different for each key if no
Gate
sync is used. Another use would be if you want to use the
Osc as an LFO, and need the modulation to always start at
a specific point (say with a square wave, at the ‘bottom’ of
the square).
For the LFO section, Gate Sync is called Retrigger,
and is accessible via the rightmost button on the
LFO panel.
Glide (rate)
Exponential glide setting for the selected oscillator, in the
range 0.0ms-20.0sec. Produces a smooth transition in pitch
between two notes.
Glide (on/off)
Enables or disables oscillator glide for the selected oscilla-
tor.
Oscillator Parameters (Mod Mode)
Oscillator
Mod
mode is active when the LED next to the
Mod label is lit.
Mod
mode loads the text display of the Os-
cillators panel with the modulation controls of the selected
oscillator. Each oscillator can have up to four modulation
sources assigned to affect various parameters.
Refer to “Modular-style Modulation” on page 18
for further explanation of Solaris’s destination-
based modulation.
The section below describes the parameters available in
each of the four oscillator
Mod
mode pages. Please refer
to “Appendix 2- Modulation Sources” on page 54 for a full
description of the oscillator modulation parameters.
Source 1-4
This control allows you to select a modulation source from
the comprehensive list of modulation sources available
within Solaris. Signal from the selected modulation source
is applied to the selected modulation destination (Dest).
Amount
This control determines the amount the control signal from
the modulation source affects the destination parameter.
When oscillator Pitch is selected as the destination, the
range of this control is -120 to + 120 semitones. When
the destination parameter is linFM or Shape, the range is
-100% to 100%.
Control
Control allows you to select another control signal to act
as a sidechain input that affects the amount of modulation
source signal that is applied to the modulation destina-
tion. The Control signal is applied to the Amount control of
the modulation source. The Strngth parameter determines
amount of Control signal to apply, in the same way that the
Amount control determines how much of the Source signal
to apply to the destination.
Strngth
Determines the amount of the Control (sidechain) signal to
apply to the Source control signal.
Dest
The destination parameter, i.e., the oscillator parameter
that will be affected by the incoming control signal from the
modulation source. The destination parameters include:
Parameter
Description
None
No parameter will be modulated
Pitch
Exponential frequency modulation of the oscil
-
lator, in semitones.
Summary of Contents for Solaris
Page 1: ...User Guide Version 1 ...