12
MSK-101-POE | Advanced configuration manual v1.1 DEC 2019 | msk-101-poe_advanced-config_en_wo v1.1 | © 2019 Inxpect SpA
l
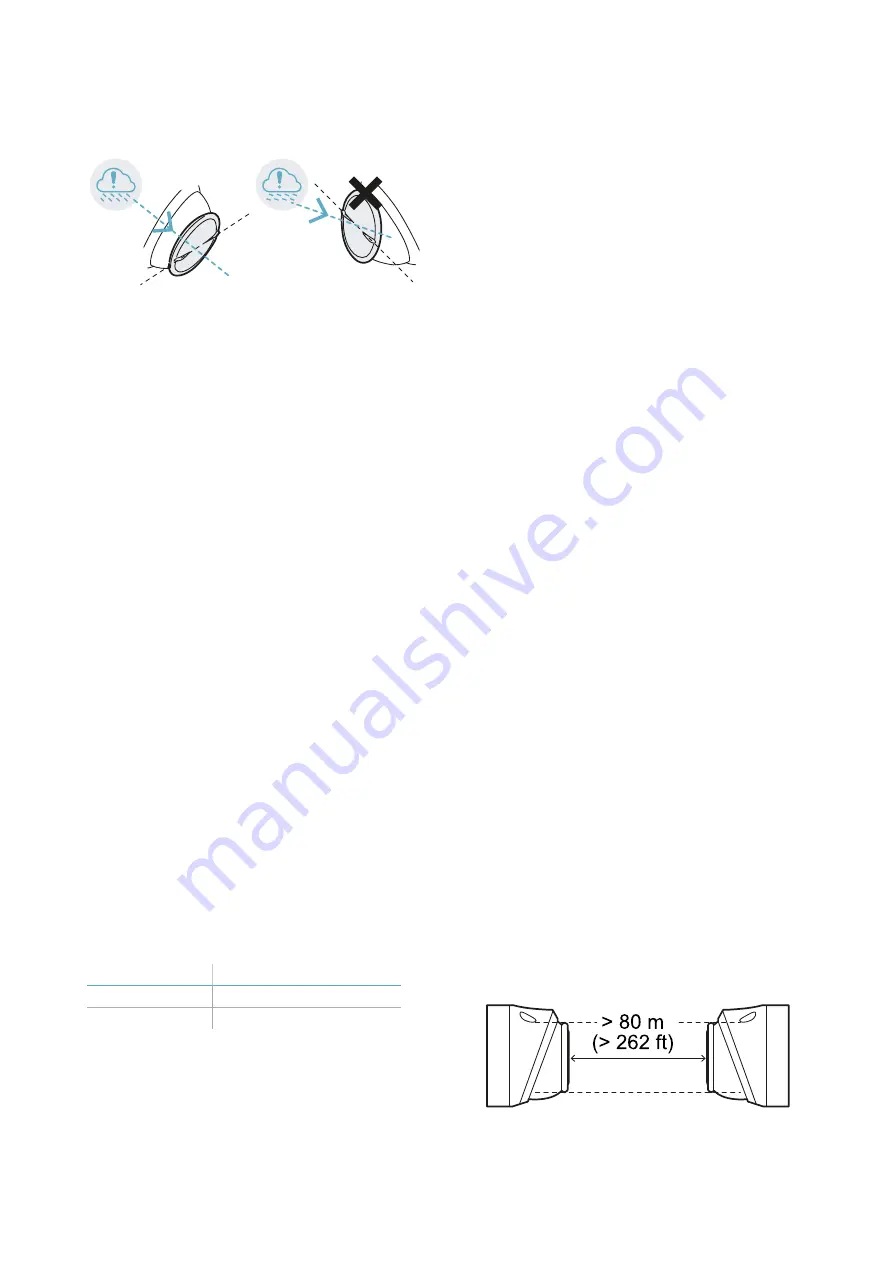
If exposed to precipitation, install the sensor
parallel to the usual direction of the
precipitation.
2.4.3 Precautions
l
The sensor has been designed for installations
on the wall or ceiling: do not install it on moving
or vibrating objects, like poles or fences.
l
Hiding the sensor behind objects may impact
the sensor performance, even significantly. To
learn about the most interfering materials, see
"Interfering materials" below.
NOTICE
: hiding the sensor is not a foreseen
use. Checking correct functioning is the
responsibility of the installer.
l
Do not install it in the presence of large
reflective objects (e.g.: metallic objects) that
could influence correct detection.
l
In the presence of fluorescent tubes, tilt down
the sensor by 15°/30°, or install it at a
minimum distance of 20 m from the tube.
l
In the presence of other MSK-101-POE
sensors, maintain the minimum indicated
distances, see "How to install several sensors"
below.
l
In the presence of other MSK-101-POE
sensors, assign each sensor to a different
channel, see "How to configure several
sensors" on the facing page.
l
The sensors that use the same frequency (e.g.
Blind Spot Detection
devices on automobiles,
with radar at 24 GHz) interfere with proper
functioning and may cause false alarms. Do
not point the sensor directly towards a parking
area.
l
The sensor can detect motion beyond glass,
walls, and thin floors, for example in drywall.
Limit the monitored area to only the specific
area of interest, and perform inspections to
prevent false alarms.
l
In the presence of neon tubes, respect the
minimum sensor inclination indicated so that
the tube does not interfere with the sensor:
Sensor direction Minimum inclination (α)*
Horizontal
- 15°
Vertical
- 30°
Note *
: see "Examples of the field of vision with
horizontal sensor direction (volumetric)" on page 10
and "Examples of the field of vision with vertical
sensor direction (barrier)" on the previous page.
2.4.4 Interfering materials
Below is a list of materials that could impact the
sensor performance if they hide it:
l
surfaces having metal-based paints or
carbon-based paints
l
tinted windows
l
surfaces having EMI/RFI glasses or mirrors
l
surfaces with water pipes, cables
l
tiles having metal-based glaze including
blue cobalt
l
metal screen foil
l
foil-backed insulation materials (e.g. foil)
l
foil moist materials (e.g. cork)
2.4.5 Factors that do NOT interfere
A list of factors that in contrast to traditional
motion sensors do NOT interfere with the normal
functioning of the sensor is presented as follows:
l
direct exposure to the sun or windows that face
the exterior
l
thin plasterboard walls or polystyrene or
stiferite panels
NOTICE
: the composition of materials used for
walls and panels is not sufficiently known to
ensure the foreseen performance of the
sensor. Checking correct functioning is the
responsibility of the installer.
l
rapid temperature fluctuations
l
smoke, dust, or strong air currents (e.g.: air
conditioners, fans)
l
water sprays, vaporized water or mist
l
electrical fields (e.g.: electrical motors, high
voltage devices)
l
moving objects (e.g.: fans, pulleys, conveyor
belts, trees and shrubs). See "Manage semi-
static objects" on page 23.
l
small animals or pets. See "Set the tolerance
level for animals" on page 22.
2.4.6 How to install several
sensors
Three possible combinations of sensor
installation and the minimum distances to
maintain between the sensors with the sensors
aligned are presented as follows. Respecting
these distances guarantees the performance
levels indicated in section "Field of vision" on
page 9.
NOTICE
: other combinations are possible, but their
performance must be validated in the field.
Front-front combination
2. Useful information for design












































