Speedway Revolution Installation and Operations Guide Octane 4.8
Chapter 3: Configuring and Monitoring
Copyright © 2011, Impinj, Inc.
19
Note
: The
show network summary
command provides the dynamic values returned by
DHCP or LLA if the current configuration is dynamic. The local hostname resolution feature
(mDNS) gives the reader a local hostname in addition to an IP address as its network
identity. On an isolated network that lacks DNS service but has mDNS enabled, a reader
with hostname speedwayr-00-01-02, for example, may be reached using
speedwayr-00-01-02.local.
4.
In Model, select the appropriate Speedway Revolution model (either Speedway R220
or Speedway R420). If you want MultiReader to issue a warning if it detects a model
other than what is configured, confirm Warn on the model mismatch checkbox is
selected. (Model mismatch is selected by default.)
5.
Configure the key RF parameters described below:
6.
Under Reader 1, on the left side of the Reader Settings dialog box, select Modes, RF,
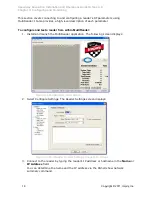
and Power. The following screen displays:
Figure 3.3 Multireader Reader Settings Settings Screen
7.
In Reader Mode, select AutoSet Dense Reader. The Reader Mode specifies the
rules to use for communication between the reader and tag. With AutoSet Dense
enabled, the reader automatically senses the environment and adjusts its mode
accordingly.
8.
In Search Mode, select Dual Target. In Session, select Session 1. Search Mode
and Session work together to control when and how often the reader reads a tag.
The high-level functional description for the reader is: Each tag contains a flag that is
flipped from A to B or from B to A when it is read. The Session value controls how
long the flag retains its value before reverting back to the original tag value. Search
Mode controls which flag values the reader reads and, in some cases, what happens
to the flag value once the tag is read.
With Dual Target, the reader reads all the tags with A flags, after reading the tags
the reader flips each tag to B. When there are no more A tags to read, the reader
reads all the B tags, flipping each one to A after it has been read. It continues this
process back and forth from A to B and back to A. Session 1 ensures a persistence
period that prevents tags from reverting before they have all been read.