4/00
UDC 3300 Controller Product Manual
217
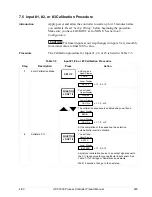
SP programming tips
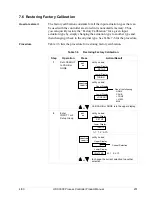
Table 6-4 gives procedures for restarting, advancing, and changing the
current segment time or setpoint of a running setpoint program.
Table 6-4
Procedures for Changing a Running Setpoint Program
Function
Press
Result/Action
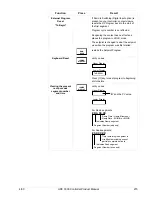
Restarting a running
SP program
RUN
HOLD
to place SP PROG into HOLD mode.
LOWER
DISPLAY
until you see X RA XXX or X SK XX.XX in
the lower display.
until you see 1 RA XX.XX in the lower
display.
If the lower display already reads 1 RA
XX.XX then press the [
▲
] key before
pressing the [
▼
] key.
RUN
HOLD
to place SP PROG into RUN mode.
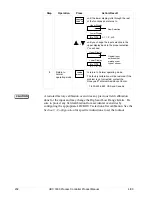
Advancing a running
SP program
RUN
HOLD
to place SP PROG into HOLD mode.
LOWER
DISPLAY
until you see X RA XXX or X SK XX.XX in
the lower display.
and
together
to select the segment number to advance to.
EXAMPLE: Change 2 SK XX.XX to 3 RA
XX.XX.
RUN
HOLD
to place SP PROG into RUN mode.
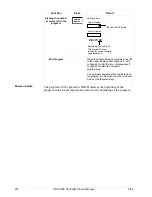
Changing the
current segment
time or setpoint in a
running SP program
RUN
HOLD
to place SP PROG into HOLD mode.
Enter SP PROG configuration and change
the segment to the new time or setpoint
desired.
LOWER
DISPLAY
until you see X RA XXX or X SK XX.XX in
the lower display.
then
RUN
HOLD
to place SP PROG into RUN mode.
Summary of Contents for UDC3300
Page 1: ...Sensing and Control UDC 3300 Universal Digital Controller Product Manual 51 52 25 55D 4 00 ...
Page 12: ...xii UDC 3300 Controller Product Manual 4 00 ...
Page 18: ...6 UDC 3300 Controller Product Manual 4 00 ...
Page 90: ...78 UDC 3300 Process Controller Product Manual 4 00 ...
Page 230: ...218 UDC 3300 Controller Product Manual 4 00 ...
Page 254: ...242 UDC 3300 Controller Product Manual 4 00 ...
Page 292: ...Index 280 UDC 3300 Controller Product Manual 4 00 ...
Page 293: ......