Chapter 7. Programming SRTP Channel Commands
124
PACSystems* RX7i & RX3i TCP/IP Ethernet Communications User Manual
GFK-2224Q
(Word 10) Time Unit for Send Period:
Words 10-11 together define how often the transfer is to be performed
(
transfer period
). Word 10 specifies the time unit such as seconds or minutes for the send period. Word 11
specifies the number of those units. The choices for the time units are shown below.
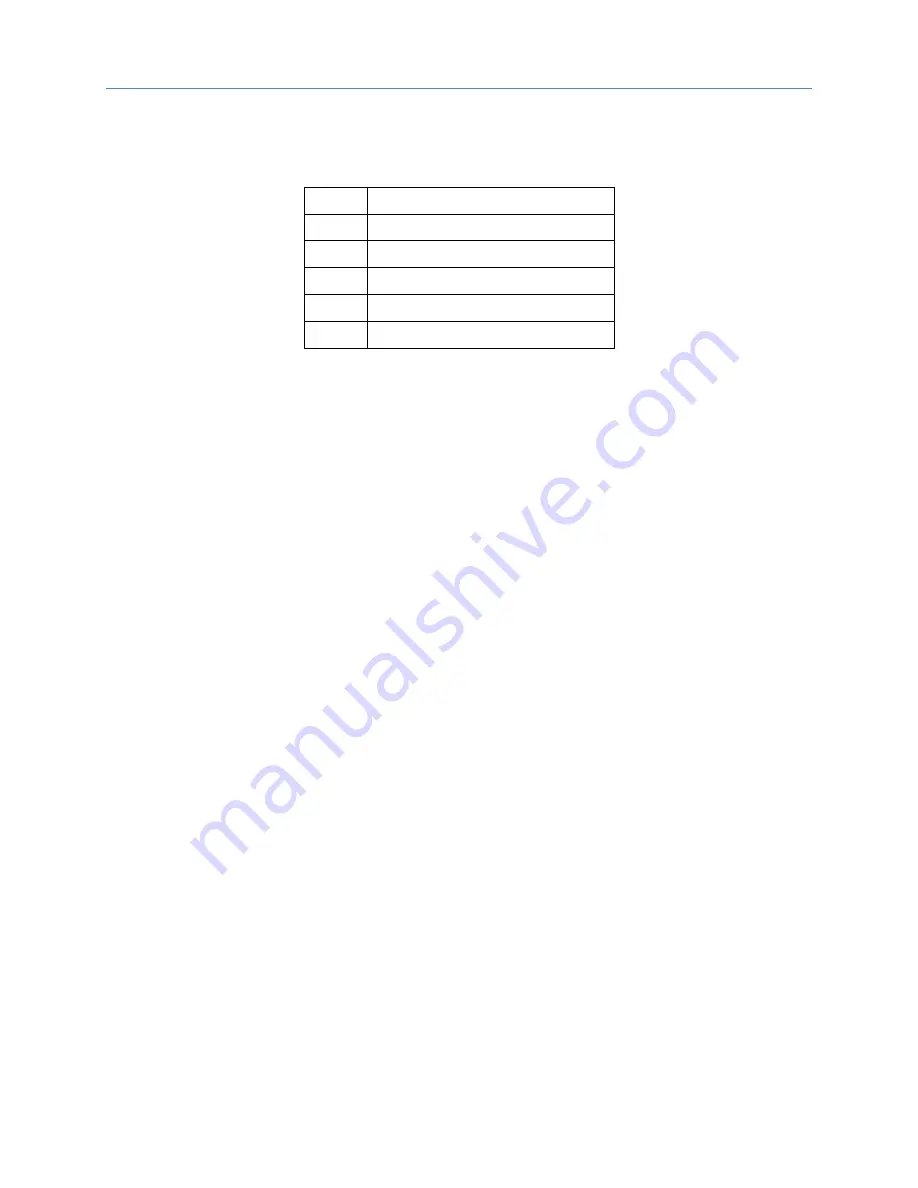
Value
Meaning
1
hundredths of seconds (10ms)
2
tenths of seconds
(100ms)
3
seconds
4
minutes
5
hours
(Word 11) Number of Time Units for Send Period:
Word 11 specifies the number of time units for the send
period. The send period is in effect even when the Channel command is set up to issue a single send.
A Channel
command set up to issue a single send can have only one
pending
send transfer.
Example Send Period Calculation:
If Word 10 contains a value of 3 specifying seconds as the time unit and
Word 11 contains a value of 20, the send period is 20 seconds.
A send is normally issued at the start of each send period. If the
pending
transfer has not completed during
the send period, the Channel Error bit and Detailed Channel Status words are set to indicate a non-fatal period
error. The pending transfer can still complete after the period error occurs. For Channel commands set up to
issue multiple sends, the next transfer is issued only after the pending transfer completes
.
If the Number of Time Units is zero, a subsequent transfer is issued as soon as the previous transfer completes.
In this case, no period errors are reported by the Channel Error bit.
(Word 12) Timeout for Each Send:
Word 12 specifies the time (in hundredths of a second) the Ethernet
Interface will wait for a send transfer to complete before setting the Channel Error bit and Detailed Channel
Status bits to indicate a non-fatal timeout error. The transfer can still complete even after a timeout occurs. As
a result, an application can choose what to do if one occurs. If the timeout value is specified as zero, no
timeout errors will be reported.
For most applications a timeout is not needed because the send period acts as a timeout. (Word 12 should be
zero for no timeout.) However, there are two circumstances where a timeout is recommended:
▪
If number of time units (Word 11) is zero, so that a subsequent transfer is issued as soon as the previous
transfer completes and no period errors are reported. In this case a timeout value can be specified so that
the Channel Error bit will report timeout errors.
▪
If the send period is very long (minutes or hours). In this case a shorter timeout value can be specified so
the application doesn’t have to wait for the send period to expire before taking action.
(Word 13) Local PLC - Memory Type:
Words 13–14 specify the location in the local PLC where the Ethernet
Interface will get the data to be written to the remote SRTP server. Valid values for Word 13 are listed for
Establish Read Channel.
(Word 14) Local PLC - Memory Starting Address:
Word 14 determines the starting address in the local PLC
from which the data is to be sent. The value entered is the offset (1-based) from the beginning of PLC memory
for the memory type and mode specified in Word 13. This offset can be in bits, bytes, or words depending on
the mode specified (for example, if Word 13=16 and Word 14=2, the starting address will be %I9). Valid ranges
of values depend on the PLC’s memory ranges.
(Word 15) Local PLC - Number of Memory Units:
Word 15 specifies the amount of data to be transferred. The
value entered is the number of memory units to be transferred, where the size of a memory unit is a bit, byte, or
word as specified in Word 13. For example, if Word 13=16 and Word 15=4, then 4 bytes (32 bits) of %I memory
will be transferred. A maximum of 16384 bits, 2048 bytes, or 1024 words of data can be specified.
(Word 16) Reserved:
Word 16 is reserved and should contain the value zero.
(Word 17) Reserved:
Word 17 is reserved and should contain the value zero.
Summary of Contents for PACSystems RX7i
Page 45: ......
Page 80: ...Chapter 4 Configuration GFK 2224Q January 2017 67 ...
Page 81: ......
Page 122: ...Chapter 6 Programming EGD Commands GFK 2224Q January 2017 109 ...
Page 147: ......
Page 211: ......
Page 262: ...Chapter 13 Network Administration GFK 2224Q January 2017 249 ...
Page 263: ......
















































