14 SYNCHRONOUS SERIAL INTERFACE (SPIA)
14-10
Seiko Epson Corporation
S1C31D50/D51 TECHNICAL MANUAL
(Rev. 2.00)
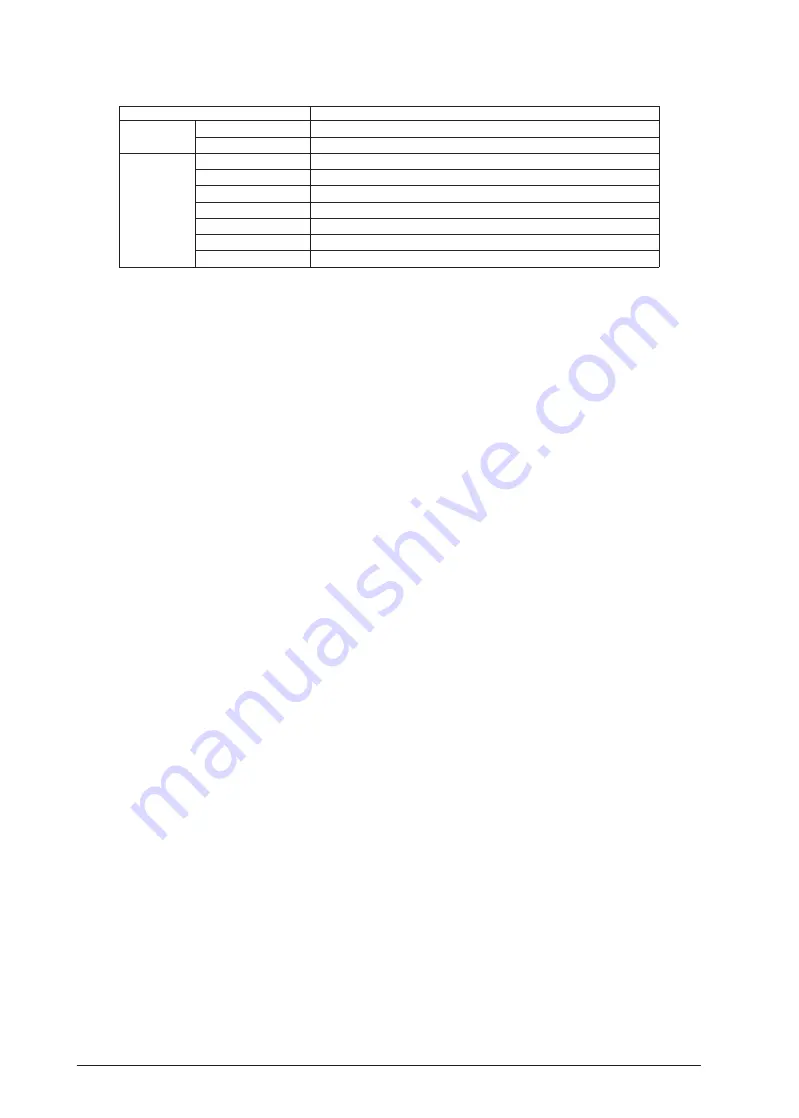
Table 14.5.3.2 DMA Data Structure Configuration Example (for 16-bit Data Reception)
Item
Setting example
End pointer Transfer source
SPIA_nRXD register address
Transfer destination Memory address to which the last received data is stored
Control data dst_inc
0x1 (+2)
dst_size
0x1 (haflword)
src_inc
0x3 (no increment)
src_size
0x1 (halfword)
R_power
0x0 (arbitrated for every transfer)
n_minus_1
Number of transfer data
cycle_ctrl
0x1 (basic transfer)
14.5.4 Terminating Data Transfer in Master Mode
A procedure to terminate data transfer in master mode is shown below.
1. Wait for an end-of-transmission interrupt (SPIA_
n
INTF.TENDIF bit = 1).
2. Set the SPIA_
n
CTL.MODEN bit to 0 to disable the SPIA Ch.
n
operations.
3. Stop the 16-bit timer to disable the clock supply to SPIA Ch.
n
.
14.5.5 Data Transfer in Slave Mode
A data sending/receiving procedure and operations in slave mode are shown below. Figures 14.5.5.1 and 14.5.5.2
show a timing chart and flowcharts, respectively.
Data sending procedure
1. Check to see if the SPIA_
n
INTF.TBEIF bit is set to 1 (transmit buffer empty).
2. Write transmit data to the SPIA_
n
TXD register.
3. Wait for a transmit buffer empty interrupt (SPIA_
n
INTF.TBEIF bit = 1).
4. Repeat Steps 2 and 3 until the end of transmit data.
Note: Transmit data must be written to the SPIA_nTXD register after the SPIA_nINTF.TBEIF bit is set
to 1 by the time the sending SPIA_nTXD register data written is completed. If no transmit data is
written during this period, the data bits input from the SDIn pin are shifted and output from the
SDOn pin without being modified.
Data receiving procedure
1. Wait for a receive buffer full interrupt (SPIA_
n
INTF.RBFIF bit = 1).
2. Read the received data from the SPIA_
n
RXD register.
3. Repeat Steps 1 and 2 until the end of data reception.
Data transfer operations
The following shows the slave mode operations different from master mode:
• Slave mode operates with the SPI clock supplied from the external SPI master to the SPICLK
n
pin.
The data transfer rate is determined by the SPICLK
n
frequency. It is not necessary to control the 16-bit timer.
• SPIA can operate as a slave device only when the slave select signal input from the external SPI master to the
#SPISS
n
pin is set to the active (low) level.
If #SPISS
n
= high, the software transfer control, the SPICLK
n
pin input, and the SDI
n
pin input are all inef-
fective. If the #SPISS
n
signal goes high during data transfer, the transfer bit counter is cleared and data in the
shift register is discarded.
• Slave mode starts data transfer when SPICLK
n
is input from the external SPI master after the #SPISS
n
signal
is asserted. Writing transmit data is not a trigger to start data transfer. Therefore, it is not necessary to write
dummy data to the transmit data buffer when performing data reception only.
















































