2 Engineering
2.9 Single-phase AC motors
DC1-S…20…, DC1-S…OE1 Variable Frequency Drives
05/21 MN040058EN
www.eaton.com
41
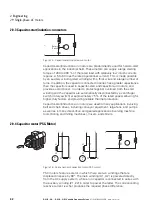
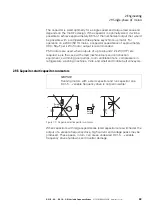
2.9.2 Split-phase motors
Figure 14: Split-phase motor
In split-phase motors, the windings inside the stator are displaced in space
and have different inductances, ensuring that the current flow through these
windings will produce the required phase difference in the magnetic fields
(approximately 25 to 30°). Within this context, the main winding has a
relatively low active resistance and a large reactance, while the start winding
has a high active resistance and a relatively low reactance.
The start winding is (must be) automatically disconnected by a centrifugal
switch (rotary switch) after about five seconds due to the risk of overheating,
as well as to reduce power loss, at approx. 75 % of the rated speed. In
applications involving refrigerator compressors, the start winding is instead
disconnected by a solenoid switch based on current consumption. The
starting torque will reach approximately 150 to 200 % of the rated torque,
and the inrush current will be around 6 to 8 times the rated operational
current.
After the start winding is disconnected, the motor will keep accelerating until
it reaches its normal speed. This speed will be relatively constant and be
approximately 2 to 5 % (slip) lower than the synchronous speed, depending
on the motor’s load.
Typical areas of application involve motor outputs of up to 300 W (0.5 HP)
with a stationary operating behavior. Examples include drives that are not
switched on and off frequently and have a low starting torque, such as those
used in small belt-drive or direct-drive machine tools, fans, compressors in
refrigerators, washing machines, oil burners, small mills, etc.
~
Rotary
Swich
U
V
Rotary
switch
n >
Summary of Contents for PowerXL
Page 4: ......