/Kits/1296-144CK.doc
10
8/15/2011
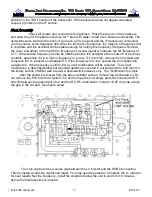
of F1 to the case. Position the shield as shown on the component placement diagram. If you are
unsure about the shield shorting the F1 filter, you may cut a small notch in the shield by C12.
5.
The RX testing is as follows. Install IC4 now if not previously done. Connect the IF port of
the transverter to a 144 MHz transceiver or spectrum analyzer and adjust R14 counter clockwise.
Inject a 1296 signal into the antenna or RX port (-30 dBm or so) with a signal generator or use a
signal on the 23 CM band. Adjust C59 and C60 for maximum signal strength on the spectrum
analyzer or in the 144 MHz transceiver. Tune for max gain. This will be very close to best noise
figure. When complete, cycle the transverter power on and off to detect the gain in the receiver. A
final adjustment will be made after the final assembly is complete so you do not need to make it
perfect. Just verify that the receiver has gain. If you have a analyzer, this would also be the time to
“Peak” F5 and F3 but it shouldn’t be necessary.
6.
Transmit testing is next. Disconnect all cables from the transverter and install the pallet into
the bottom enclosure Start all 6 of the 4-40 x 7/16” screws. Do not tighten. Start the rear panel
screws. Then install the front panel and gradually tighten all of the 10 screws together to ensure a
good fit. Tighten everything evenly to be sure that the pallet is resting on the ribs in the enclosure.
Be sure not to pinch any wires. Connect a 50 ohm load either on the TXRF port or the antenna
connector. Then connect the DC voltage and power it on. To test the TX voltages, key the PTT
line (PTT-H or –L) and measure to verify against the TX voltage matrix. If any voltage is out of
tolerance, verify all surrounding components and recheck bottom side wiring. Remember, MMICs
draw a specified amount of current but may be a bit out of tolerance
LOCATION
TX VOLTAGE Matrix referenced to Ground
Output of VR3 (C55)
+9.0 VDC
±
0.3V
Junction of IC6 and C38
+2.5 VDC
±
0.5V
Junction of IC6 and C39
+4.5 VDC
±
0.5V
Junction of IC7 and C39
+1.5 VDC
±
0.5V
Junction of IC7 and C42
+6.0 VDC
±
1.0V
Junction of R12 and D2
+1.6 VDC
±
0.3V
Junction of D3 and L10
+0.7 VDC
±
0.3V
Junction of D1 and K3
+13.8 VDC (if K3 is not installed, no need to test)
Junction of D7 and K1
+13.8 VDC (if K1 is not installed, no need to test)
Junction of L30 and C53
+9.0 VDC
±
0.3V
7.
To RF test the transmit section, If you need to use your 2 meter transceiver, install the 50
ohm load if it is required for your configuration. Connect a power meter that can measure 5 watts
@ 1296 MHz to the TXRF or ANT connector Connect your IF drive source to the BNC connector
(common IF or TXIF). Check your drive power level before applying drive. Adjust R20 clockwise
for maximum attenuation. Key the PTT line and apply TX drive either from your generator or
transceiver and adjust the R20 to obtain a desired output power. The output power will depend on
the IF drive level setting of R20. If you cannot obtain the correct output power by adjusting R20,
check your configuration and measure your drive level. Do not assume that there is too much
attenuation in the IF section if the unit will not make the output power specification and change the
attenuation values. If the IF is configured for a lower drive level, damage may occur to the mixer if
it is over driven even for a short period of time. If you have variable output power on your 2 meter
transceiver or generator, set it to the minimum and raise it until saturation occurs. This is when the
output power does not increase when the drive level is increased. If this happens, suspect a
Summary of Contents for 1296-144 CK
Page 16: ......