Gratuitous ARP
Ethernet Header
Destination
address
Source address Ethernet
type
H/W type
Protocol
type
H/W
address
length
Protocol
address
length
Operation
Sender H/W
address
Sender
protocol
address
Target H/W
address
Target
protocol
address
(6-byte) (6-byte)
(2-byte)
(2-byte)
(2-byte)
(1-byte)
(1-byte)
(2-byte) (6-byte) (4-byte) (6-byte) (4-byte)
FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF 00-20-5C-01-11-11
806
ARP reply
00-20-5C-01-11-11
10.10.10.254
00-20-5C-01-11-11
10.10.10.254
Table - 5
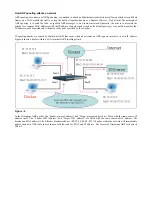
A common DoS attack today can be done by associating a nonexistent or any specified MAC address to the IP address of the
network’s default gateway. The malicious attacker only needs to broadcast ONE Gratuitous ARP to the network claiming it is the
gateway so that the whole network operation will be turned down as all packets sent through the Internet will be directed to the
wrong node.
Likewise, the attacker can either choose to forward the traffic to the actual default gateway (passive sniffing) or modify the data
before forwarding it (man-in-the-middle attack). The hacker fools the victims PC to make it believe it is a router and fools the
router to make it believe it is the victim. As can be seen in Figure-5 all traffic will be then sniffed by the hacker without the users
knowledge.
Figure - 5
Summary of Contents for DES-3028
Page 306: ......
Page 307: ......
Page 327: ...D Link D Link D Link D Link 7 495 744 00 99 http www dlink ru e mail support dlink ru...
Page 332: ...Technical Support Web Web URL http www dlink jp com...