48
2. Networks
PC Functions
Setting Up Wireless
Networks (WLAN)
Three steps are required to integrate your multifunction
machine into a wireless network (WLAN):
1
Configure the network on your PC.
2
Configure your multifunction machine for net-
work operation.
3
Install the software Companion Suite IH with the
required printer drivers on your PC after you have
configured the machine.
Æ
Before you configure the multifunction ma-
chine, the network must be set up on your PC
and, if applicable, on all connected devices (other
PCs, access point, gateway, router) and must be
functioning. All required information for config-
uration of the machine, such as network names
(SSID), radio channel, WEP key, IP address or
subnet mask must match the information of the
network. You can find this information on your
PC under Start > Settings > Network Con-
nections. Select the WLAN there. Consult the
user manual of your WLAN adapter for instruc-
tions on how to configure the wireless network
on your PC. In larger networks, consult your
network administrator.
²
Faultless communication is ensured if you
also use an original adapter on your PC.
Setting Up the Multifunction
Machine
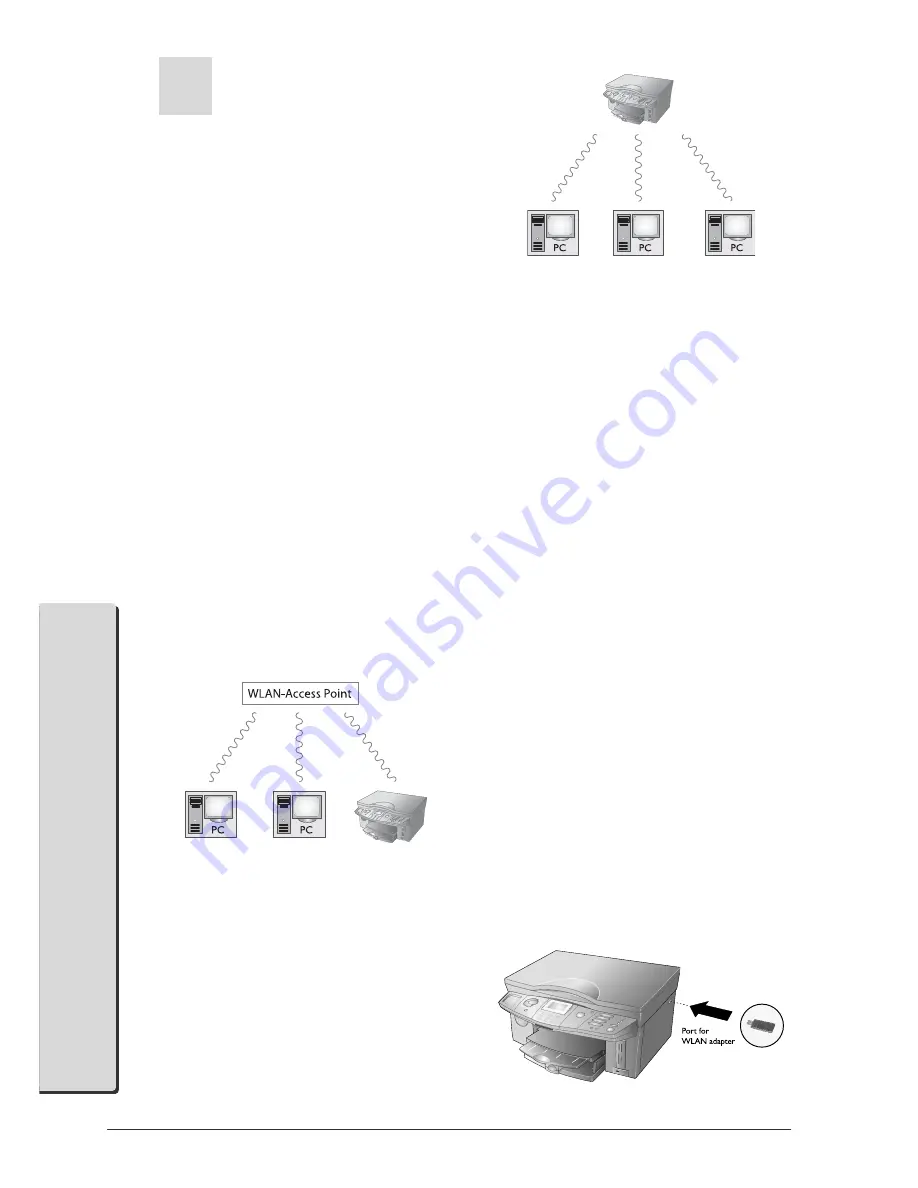
Insert the WLAN adapter into the side USB port of
your machine.
2.
Networks
You can connect your multifunction machine to a PC
with a USB cable or to a PC or network via a wireless
connection.
With the USB cable, you can connect your
multifunction machine to a PC that is connected to a
network. Other PCs on this network can then access
the multifunction machine if it is shared for use on the
network. You cannot connect the machine directly to
a network over the USB cable!
With a WLAN adapter, it is possible to integrate the
multifunction machine into an existing wireless net-
work as a network printer. It functions only with an
original adapter.
Wireless Networks
One refers to a wireless network or WLAN (Wireless
Local Area Network) if at least two computers, printers
or other devices communicate in a network over radio
waves (high frequency waves). The data transmission
in the wireless network is based on the TCP/IP proto-
col. Depending on the way the network is structured,
it is referred to either as an infrastructure or ad-hoc
network.
Infrastructure Wireless Network
In an infrastructure network, multiple devices com-
municate via a central access point (gateway, router).
All data are sent to the access point (gateway, router)
and distributed from there.
Ad-hoc Wireless Network
In an ad-hoc network, the devices communicate with
each other equally, without an access point (gateway,
router) acting as intermediary. The transmission rate
in an entire ad-hoc wireless network depends on the
worst connection in the network. The transmission
rate depends on the spatial distance as well as obsta-
cles between the sender and receiver such as walls or
ceilings.
Summary of Contents for Belgafax 710
Page 2: ......
Page 68: ...68 Appendix...
Page 69: ...Appendix 69 Appendix...
Page 70: ...70 Appendix...
Page 71: ......






























