page 70
page 70
page 70
page 70
page 70
375 SE
800-00162
SINGLE PUMP MAINTENANCE CONTINUED...
V - SERVICE, INSPECTION, AND MAINTENANCE
V - SERVICE, INSPECTION, AND MAINTENANCE
V - SERVICE, INSPECTION, AND MAINTENANCE
V - SERVICE, INSPECTION, AND MAINTENANCE
V - SERVICE, INSPECTION, AND MAINTENANCE
A. SERVICE TOOLS
A. SERVICE TOOLS
A. SERVICE TOOLS
A. SERVICE TOOLS
A. SERVICE TOOLS
Two special tools are required to service these pumps. A driver should be used to assure installation of the primary shaft
seal without damage, and a “bullet” should be placed over the end of the shaft, to avoid damaging the seal lip when the
shaft is installed. Installation of the secondary seal does not require a driver. (See Figure 5).
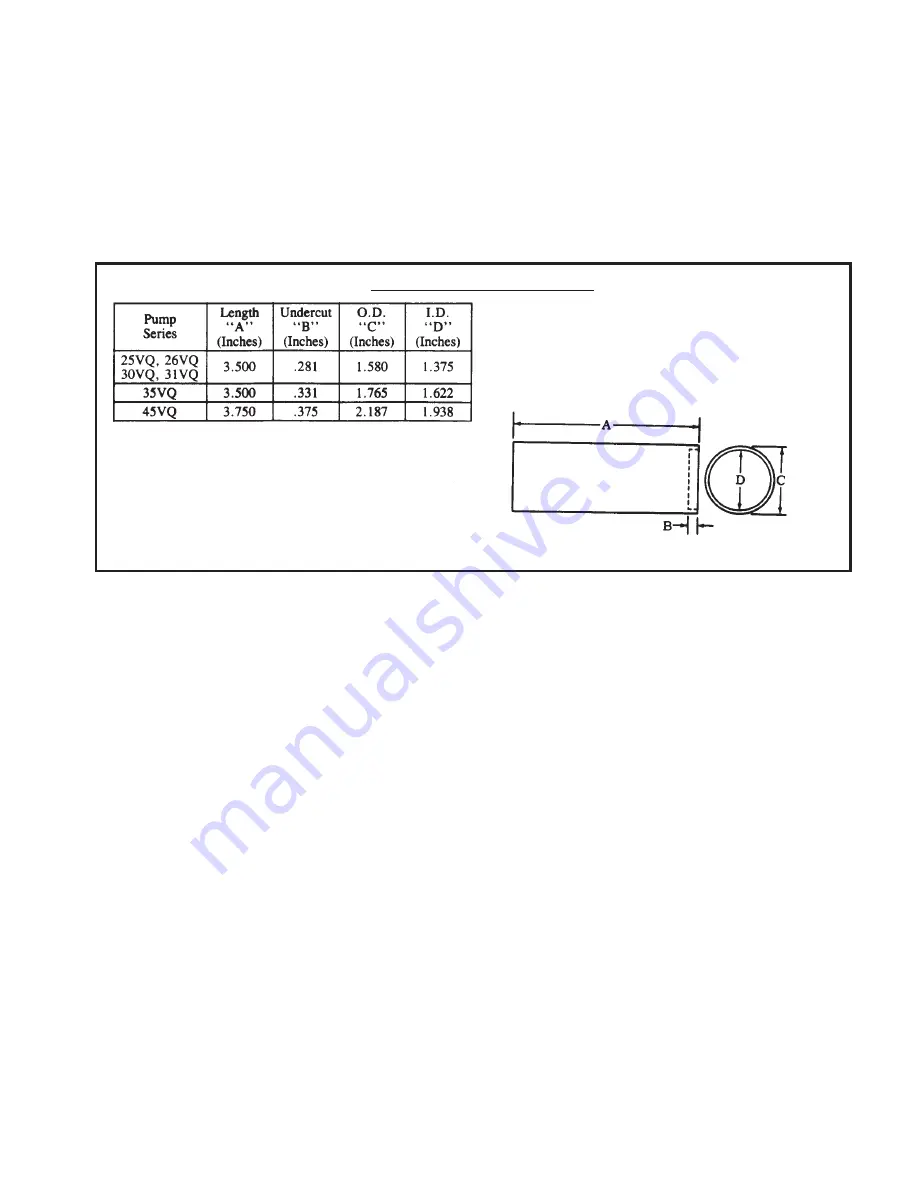
The driver can be made from tubular stock as shown in Figure 6. The tool applies a uniform pressure to the recessed
area of the seal, rather than to the lip of the seal. The inside diameter of the tool will not interfere with the garter spring
located around the lip of the seal.
B. INSPECTION
B. INSPECTION
B. INSPECTION
B. INSPECTION
B. INSPECTION
Periodic inspection of the fluid condition and tube or piping connections can save time-consuming breakdowns and
unnecessary parts replacement. The following should be checked regularly.
1. All hydraulic connections must be kept tight. A loose connection in a pressure line will permit the fluid to leak
out. If the fluid level becomes so low as to uncover the inlet pipe opening in the reservoir, extensive damage
to the pump can result. In suction or return lines, loose connections permit air to be drawn into the system,
resulting in noisy and/or erratic operation.
2. Clean fluid is the best insurance for long service life. Therefore, the reservoir should be checked periodically
for dirt or other contaminants.
If the fluid becomes contaminated the system should be thoroughly drained and the reservoir cleaned
before new fluid is added.
3. Filter elements also should be checked and replaced periodically. A clogged filter element results in a higher
pressure drop. This can force particles through the filter which would ordinarily be trapped, or can cause the
by-pass to open, resulting in a partial or complete loss of filtration.
4. Air bubbles in the reservoir can ruin the pump and other components. If bubbles are seen, locate the source
of the air and seal the leak. (See Table 1).
5. A pump which is running excessively hot or noisy is a potential failure. Should a pump become noisy or
overheated, the machine should be shut down immediately and the cause of improper operation corrected.
C. ADDING FLUID TO THE SYSTEM
C. ADDING FLUID TO THE SYSTEM
C. ADDING FLUID TO THE SYSTEM
C. ADDING FLUID TO THE SYSTEM
C. ADDING FLUID TO THE SYSTEM
When hydraulic fluid is added to replenish the system, it should always be poured through a fine wire screen (200 mesh
or finer) or preferably pumped through a 10 micron (absolute) filter.
It is important that the fluid be clean and free of any substance which could cause improper operation or wear of the
pump or other hydraulic units. Therefore, the use of cloth to strain the fluid should be avoided to prevent lint getting into
the system.
PRIMARY SHAFT SEAL DRIVER
PRIMARY SHAFT SEAL DRIVER
PRIMARY SHAFT SEAL DRIVER
PRIMARY SHAFT SEAL DRIVER
PRIMARY SHAFT SEAL DRIVER
FIGURE 6
FIGURE 6
FIGURE 6
FIGURE 6
FIGURE 6






























