30 |
Baker Hughes
© 2020 Baker Hughes Company. All rights reserved.
XVII. Troubleshooting Guide for Safety Valves
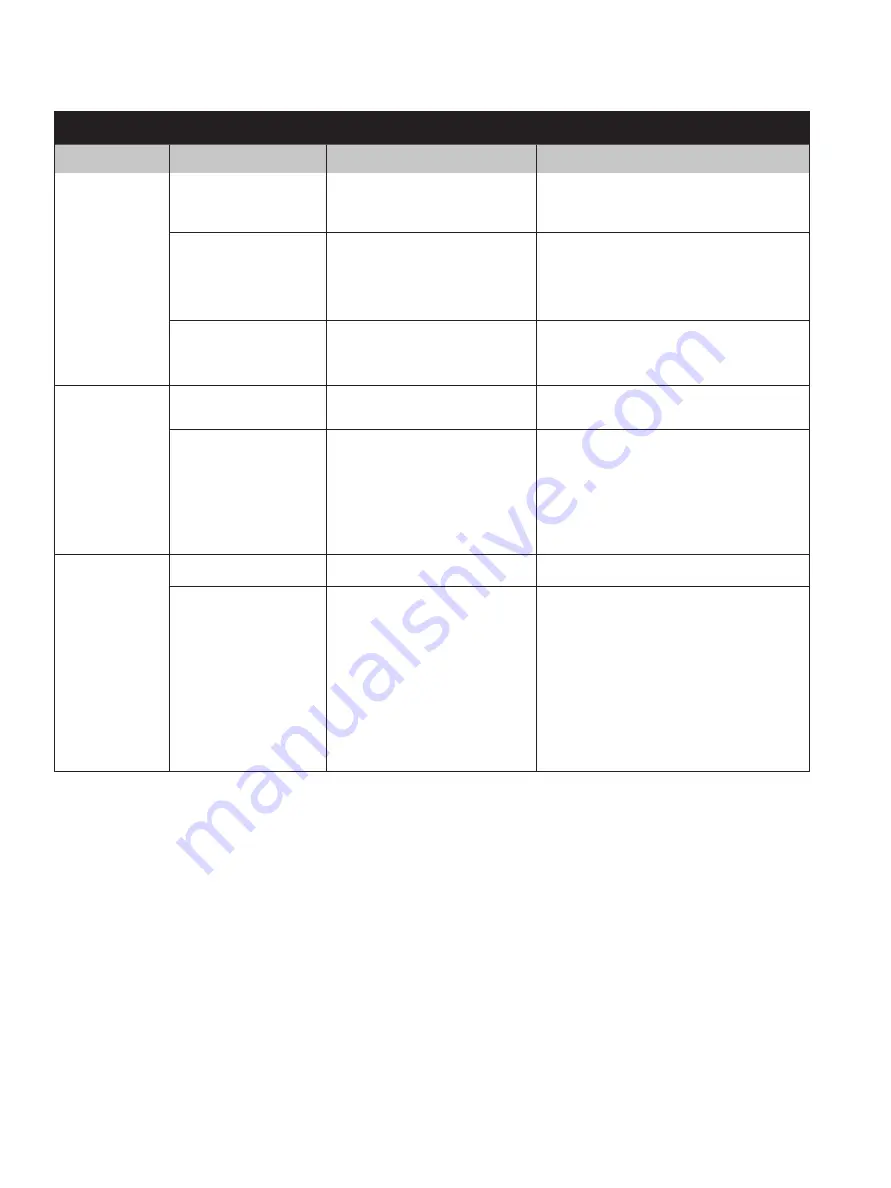
Table 12: Troubleshooting Guide
Problem
Specific
Probable Cause
Corrective Action
Opening
Simmer
• Operating pressure to close to
set pressure
• Increase differential
• Adjusting ring too low
• Raise ring
Chatter
• Flow starved
• inlet pressure drop too large
• See Figure
9
• built up back pressure
• Check discharge piping
• valve too large
• Check piping system
Erratic Set
• Mechanical bind
• Check valve piping
• Temperatures differential
• Stabilize valve temperature
• Fatigued spring
• Replace Spring
Closing
Long Blowdown
• Adjusting ring too high
• Lower ring
• Hang-up
• See “Closing/Hang-up”
Hang-up
(does not fully close)
• Adjusting Ring too high
• Lower ring
• Pipe Loads
• See Figure
9
• Misalignment of Parts
• See Figure
9, be sure valve is vertical and
properly reassembled
• Mechanical binding
• Improper valve assembly
• Corrosion
• Improper material selection
Seat Leakage
Simmer
• See “Opening”
• See “Opening”
Leakage
• Vibration
• Check piping system
• Piping loads
• See Figure
9
• Operating pressure too close to
set pressure
• Increase differential
• Solids trapped on seat
• Lift lifting lever if equipped or inspect for
seat damage
• Mechanical binding
• See “Closing/Hang-up”
• Improper assembly
• Remove valve and inspect parts
• Valve oversized
• Recheck piping system
Note:
For Valve Terminology see Section V.
XIX. 1900/P Series SV Options
A. Cap and Weather Shield
Options
Steam Internals caps are supplied in accordance with customer
order and/or the ASME Code. All caps for the same size valve
are interchangeable and are available with or without gag.
Manual Popping: on steam application after the valve has been
in use, it may be necessary when permitted:
• to lift the disc from the valve seat periodically during
operations to ensure that the disc is not frozen, etc. as a
result of corrosion/boiler water deposits. Operating pressure
under the disc should be approximately 75 percent of the
set pressure when lifting in accordance with the ASME
Code; otherwise, the lever assembly including spindle may
be damaged.
• to dislodge foreign particles that sometimes become
trapped on the seating surface as the valve recloses.
Prompt lifting of the lever, using system fluid pressure to
clean the seat, should correct an otherwise leaking valve
and save maintenance costs at a later date.
Refer to Figure
28 for more information.











































