IFD400 Series Pilot Guide
Navigation 5-35
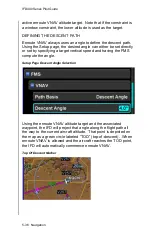
ENROUTE VERTICAL NAVIGATION (VNAV)
The IFD is capable of providing vertical navigation during descent
operations.
Vertical navigation is driven by a “descent path” that
is defined by the altitude constraints in the flight plan and a
descent angle specified on the Setup page. When enroute VNAV
is active, the IFD will provide vertical deviations to the descent
path. The enroute VNAV capability must be enabled by the
installer after it is determined that the aircraft is equipped to
perform the function.
ALLOWING ENROUTE VNAV
The following conditions must be satisfied in order for enroute
VNAV to be allowed:
Enroute VNAV is enabled by the installer
The flight plan has an active leg
The aircraft is airborne
The IFD is receiving a valid baro corrected altitude
If enroute VNAV is not allowed, enroute vertical deviations will not
be generated. However, the IFD will still compute the top-of-
descent (TOD) point using VNAV descent angle or rate.
DEFINING THE ENROUTE VNAV ALTITUDE TARGET
Altitude constraints entered into the flight plan define the potential
altitude targets for enroute VNAV. The IFD evaluates each
successive leg of the flight plan, starting with the active leg, to
determine the active enroute VNAV altitude target. If the leg
begin evaluated meets any of the following criteria, the IFD stops
searching and there is no enroute VNAV altitude target:
The leg terminates at an altitude
The leg is a hold
The leg terminates at a FAF
The leg is preceded by a discontinuity (except the active
leg)
If the leg has an associated altitude constraint whose altitude is
lower than the aircraft altitude, the IFD uses that altitude as the
Summary of Contents for IFD410 FMS/GPS
Page 1: ......
Page 8: ......
Page 56: ......
Page 100: ...IFD400 Series Pilot Guide 2 44 FMS Subsystem Info Tab Nearby Navaids ...
Page 160: ......
Page 250: ...IFD400 Series Pilot Guide 4 90 Aux Subsystem ADS B Unavailable Products Page ...
Page 252: ......
Page 378: ......