37
+
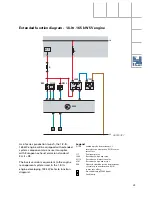
G130
1
2
3
4
J220
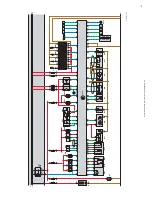
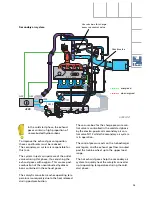
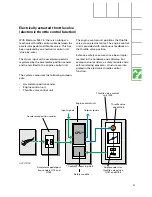
Electrical circuit
SSP207/101
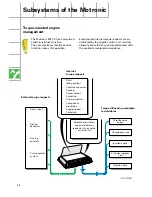
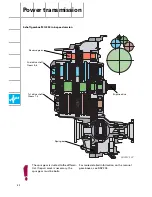
Subsystems of the Motronic
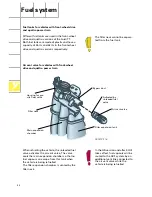
Catalytic conversion diagnosis
During the diagnosis, the engine control unit
compares the probe stresses upstream and
downstream of the catalytic converter probe
and calculates an upstream-to-downstream
ratio.
If this ratio deviates from the nominal range of
values, the engine management recognises
that the catalytic converter has malfunctioned.
After the fault conditions have been fulfilled,
the appropriate fault code is saved to the fault
memory.
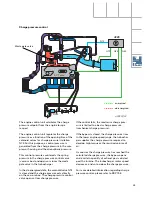
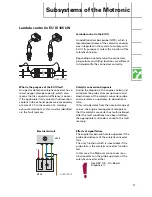
Lambda control in EU III 165 kW
What is the purpose of the EU III test?
An aged or defective catalytic converter has a
lower oxygen storage capacity, which also
means that its conversion efficiency is poorer.
If the applicable limit values for hydrocarbon
content in the exhaust gases are exceeded by
a factor of 1.5 in the course of a statutory
exhaust emission test, this must be identified
via the fault memory.
SSP207/100
Lambda control in the EU III
An additional lambda probe (G130), which is
located downstream of the catalytic converter,
was integrated in the system to comply with
EU III. Its purpose is to test the function of the
catalytic converter.
Depending on vehicle type, the connectors,
plug colours and fitting locations are different
to help identify the connectors correctly.
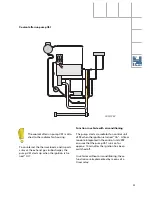
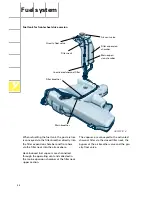
Effects of signal failure
The engine lambda control also operates if the
probe downstream of the catalytic converter
fails.
The only function which is unavailable if the
probe fails is the catalytic converter function
test.
In this case, the Motronic cannot execute a
functional test on the probe upstream of the
catalytic converter either.
See SSP 175 – On-Board
Diagnosis II.