98
Chapter 5
Dual Arbitrary Waveform Generator
Arbitrary (ARB) Waveform File Headers
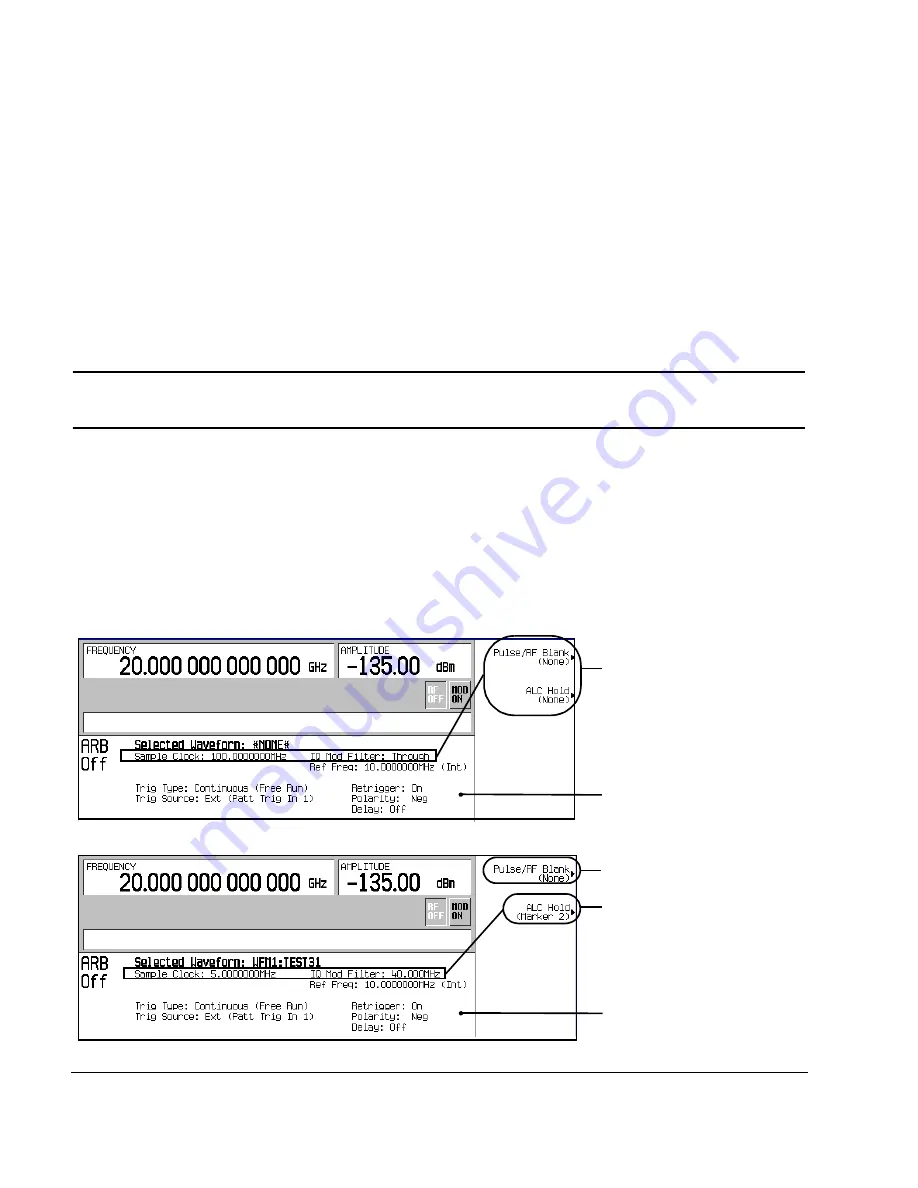
Playing a Waveform File that Contains a Header
After a waveform file (AUTOGEN_WAVEFORM) is generated in a modulation format and the format is
turned off, the file becomes accessible to and can be played back in only the dual ARB player. This is also
true for downloaded waveform files (downloading files is described in the Programming Guide). When the
waveform is selected for playback, the saved header information is used by the signal generator. Some of
these settings appear as part of the labels of the softkeys used to set the parameters, and also appear on the
dual ARB summary display (see
Figure 5-8
).
NOTE
The signal generator used to play back a stored waveform file must have the same options
as are required to generate the file.
For details on applying file header settings and playing back a waveform, see
“Playing a Waveform” on
page 102
.
To properly set up the instrument:
1. Select the waveform.
2. Modify the signal generator settings as desired.
3. Turn on the dual ARB.
Figure 5-8
File Header Settings
Header setting same as
preset setting
Header setting applied
Summary Display
The waveform is selected;
saved header settings are
applied.
Can change when a
waveform is selected
Summary Display
The waveform is not selected;
preset settings are applied.
Summary of Contents for E8247C
Page 10: ...Contents x ...
Page 96: ...86 Chapter 4 Analog Modulation Configuring the LF Output ...
Page 142: ...132 Chapter 6 Custom Arb Waveform Generator Working with Filters ...
Page 178: ...168 Chapter 7 Custom Real Time I Q Baseband Working with Differential Data Encoding ...
Page 198: ...188 Chapter 10 Troubleshooting ...
Page 214: ...204 Chapter 10 Troubleshooting Returning a Signal Generator to Agilent Technologies ...






























