57
Zehnder Eversky
21.3. Alarm actions
In addition to its class, each alarm is defined by an action.
The action of an alarm defines the behaviour of the machine when the corresponding alarm occurs. There are several
actions:
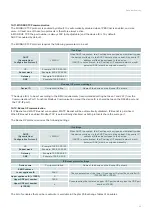
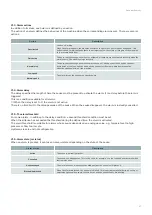
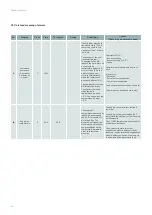
Action
Description
Deactivated
Used as a warning.
When the alarm appears, the machine continues to operate as if nothing has happened. This
action is used for malfunctions that are not important for the safety or integrity of the machine
(e.g. pressure deviation).
Quick stop
The post-ventilation sequence is not considered, all outputs are deactivated instantly when the
alarm occurs. The machine stops instantly.
Normal stop
The post-ventilation sequence is taken into account. This sequence is defined by the shut-
down times of the fans and the fresh air and exhaust air dampers, which determine the
effective shut-down time of the machine.
Low speed
The alarm forces the configured speed regime.
Normal speed
21.4. Alarm delay
The delay specifies the length of time the cause must be present to activate the alarm. It is a delay before the alarm is
triggered.
This is a condition available for all alarms.
/!\ When the delay is set to 0, the alarm is not active.
There is no time limit to the disappearance of the cause. When the cause disappears, the alarm is instantly cancelled.
21.5. The alarm threshold
For some alarms, in addition to the delay condition, a second threshold condition must be set.
When the criterion has exceeded the threshold during the defined time, the alarm is activated.
The alarm threshold is available for alarms whose cause depends on an analogue value, e.g. temperature too high,
pressure or flow too low, etc.
Hysteresis is zero and not configurable.
21.6. Alarm state (or status)
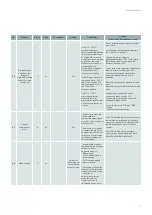
When an alarm is present, it can take on several states depending on the state of the cause:
Alarm status
Description
Active
The cause is currently present.
Cancelled
The cause has disappeared. This is the case, for example, of a fan runback air pressure switch
that remains open.
Acknowledged
The alarm has been manually acknowledged (but the cause is still present).
Blocked/Unblocked
When the alarm is blocked, the action is inhibited. This is particularly useful during a set-up or
adjustment phase when some sensors have not been connected or are missing.