Antenna Basics
Version 1.0 Rev B - 08/00
83
Factor
Description
Maximizing the
Hopper Plus 120-
24’s Capabilities
• Minimize obstructions in the radio path.
• Line Of Sight (LOS) is crucial for reliability.
• Ensure that equipment is installed correctly.
• Ensure proper grounding, testing, and alignment of antennas.
• Install in environmental conditions that are suitable for the
Hopper Plus 120-24.
• Select proper antennas and cable for the application.
• Ensure sufficient gain for the intended application.
Safety
• Proper grounding of antenna apparatus in accordance with
respective Electrical Code(s) is crucial.
• Wi-LAN recommends using a surge arrestor where the antenna
cable enters the building.
• All installations should be completed by a qualified and
competent RF technician.
EIRP
• Effective Isotropically Radiated Power (EIRP)
• EIRP is the amount of power that is transmitted to the air from
the antenna.
• EIRP levels depend on the power of the radio transmitter, the
size of the antenna, and the losses incurred in the antenna
cable.
• To remain license-exempt the EIRP must remain under 4 watts
or 36 dBm in Canada and the United States for
point-to-multipoint applications. In Europe, this value is reduced
to 100 mW or 20 dBm.
Note:
EIRP = Power out of unit – Power lost in cable + Gain in
power from Antenna
Fade Margin
See
Calculating Fade Margins
on page 72.
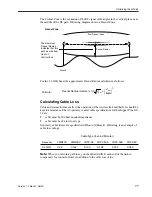
LOS
• Line of Sight (LOS)
• LOS is a football shaped pattern known as the Fresnel Zone,
which must be kept clear of obstructions. See
Working with the
Fresnel Zone
on page 76 for more information.
• Visual line of sight must be achieved. When standing at the
antenna position, you must be able to see the remote antenna.