Printed in the Federal Republic of Germany
TR-Electronic GmbH 2008, All Rights Reserved
06/27/2017
TR - ECE - BA - DGB - 0073 - 07
Page 87 of 155
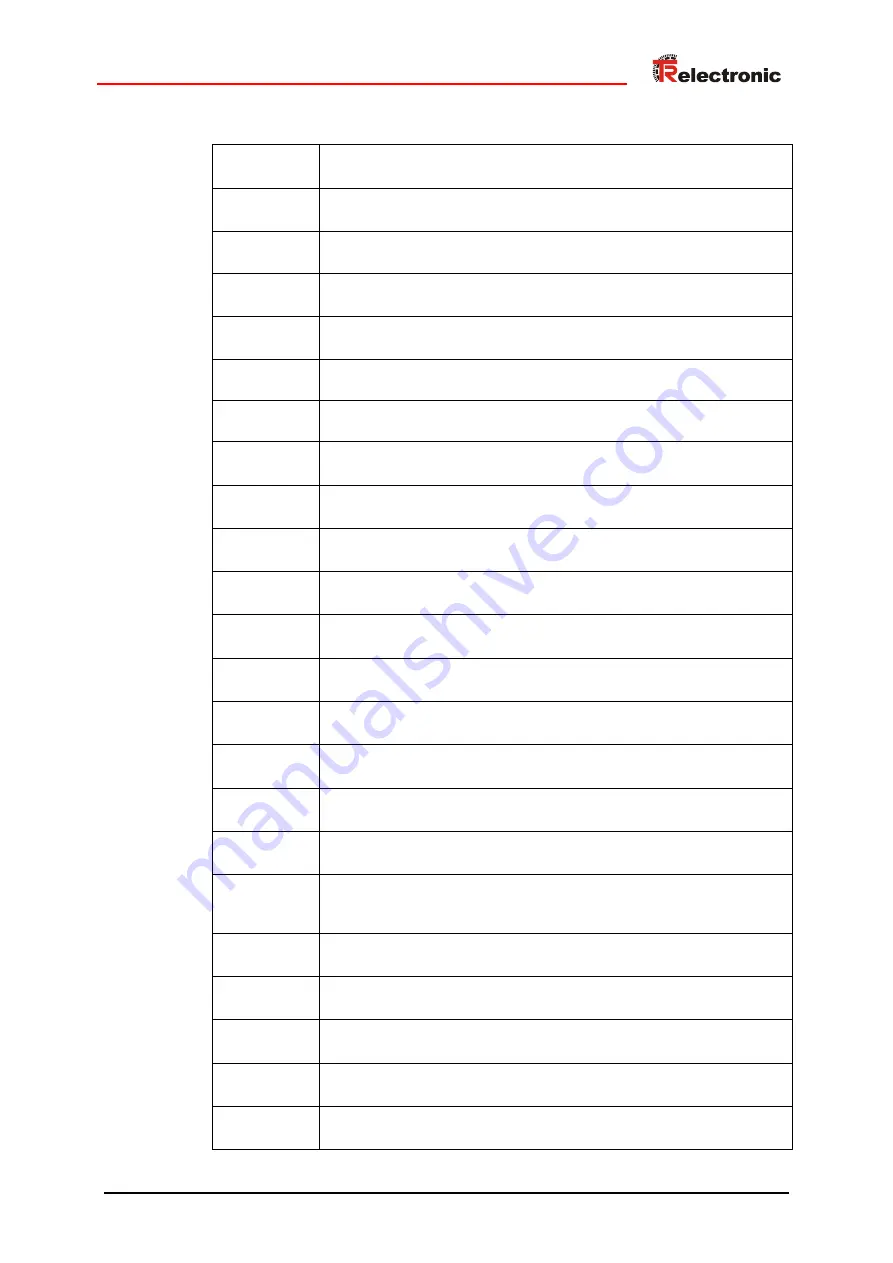
1.3 Abbreviations used / Terminology
CAN
C
ontroller
A
rea
N
etwork
(manufacturer independent, open field bus standard)
CEK
Absolute Encoder with optical scanning unit,
Integrated Claw Coupling
CES
Absolute Encoder with optical scanning unit
15 bit resolution,
Blind Shaft
CEV
Absolute Encoder with optical scanning unit
15 bit resolution,
Solid Shaft
CIP
™
C
ommon
I
ndustrial
P
rotocol, protocol for transmission of real time
data and configuration data.
COS
Absolute Encoder with optical scanning unit > 15 bit resolution,
Blind Shaft
COV
Absolute Encoder with optical scanning unit > 15 bit resolution,
Solid Shaft
DHCP
D
ynamic
H
ost
C
onfiguration
P
rotocol,
dynamic assignment of an IP address
DNS
D
omain
N
ame
S
ystem, Name resolution into an IP address
EDS
E
lectronic-
D
ata-
S
heet
EMC
E
lectro
M
agnetic
C
ompatibility
Gateway
Interconnect point between two networks
Half-Duplex
Unidirectional data transmission
IGMP
I
nternet
G
roup
M
anagement
P
rotocol,
protocol for management of groups
MAC-ID
M
edia
A
ccess
C
ontrol
Id
entifier
(node address)
Multicast
Multi-Point-Connection, the message is sent to a certain group of
subscribers in the network.
ODVA
™
O
pen
D
eviceNet
V
endor
A
ssociation
(CAN User Organization, especially for DeviceNet
, EtherNet/IP™)
Port
Connection,
Part of an address, which allocates data segments to a network
protocol.
Router
Network component to couple several subnets.
Switch
Network component to connect several computers or net segments
within a local network, avoid collisions.
TCP/IP
T
ransmission
C
ontrol
P
rotocol/
I
nternet
P
rotocol
UDP
U
ser
D
atagram
P
rotocol
Full-Duplex
Bidirectional data transmission