5-12
ET 200U Distributed I/O Station
EWA 4NEB 812 6087–02b
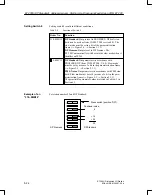
Table 5-4
Address IDs for the Modules in an ET 200U(DP Standard) Station
Order No. of
Module
Address ID
ET 200U(DP Standard)
Address
Scope
(Byte)
Delay
Time
(ms)
1
Ad-
dress
Area
Current
Con-
sumption
Power
Loss
(W)
Order Code
Decimal No.
(Byte)
(ms)
1
Area
sumption
(mA)
(W)
Input/Output Module:
482–8MA11
–8MA12
–8MA13
–
049 or 112
1
2*
Digital
or
analog
50
4.5
Power Supply Module:
935–8ME11
2
8DI/8DI
016/016
–
Digital
7.5
Simulator Module:
788–8MA11
8DI
016
1
< 0.2
Digital
30
0.3
8DQ
032
1
Digital
30
Timer Module:
380–8MA11
8DX
048
1*
Digital
10
Counter Modules:
385–8MA11
8DX
048
1*
0.18
Digital
20
2.5
385–8MB11
2AX
241
4*
Analog
70
1.9
Comparator Module:
461–8MA11
8DI
016
1
5
Digital
35
0.3
PID Controller Modules:
3
262–8MA11
–8MA12
4AX
243
8*
100 ...
200
Analog
20
262–8MB11
–8MB12
4AX
243
8*
100 ...
200
Analog
20
Position Control Modules:
263–8MA11
2
4AX/000
243/000
8*
Analog
120
4
266–8MA11
4AX
243
8*
Analog
267–8MA11
2AX
241
4*
Analog
150
*
The address scope is necessary for the inputs and the outputs (i.e. if the address scope is 2 bytes, 2 bytes are used
for the inputs and 2 bytes are used for the outputs). Since COM ET200 assigns the addresses for these modules
optionally, inputs and outputs can have different start addresses.
1
The module can also be addressed as 1–channel analog module
2
The module occupies 2 slots.
3
You can address a PID controller module in an ET 200 system at least every 200 ms. You cannot use function
blocks FB61 and FB62.
ET 200U(DP Standard): Address Assignm.,Starting–Up, Diagnosing Faults Using COM ET 200