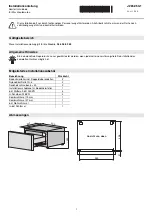
Figure 3: Measurement principle of the 2D laser scanner
3.6.2
Range finding
The device emits beams pulsed by a laser diode. If a laser pulse hits an object or per‐
son, it is reflected on the surface of the object or person in question. The reflection is
registered by a photosensitive element in the device receiver. The device uses SICK’s
own HDDM/HDDM+ (High Definition Distance Measurement) technology. With this
measurement process, a measured value is formed by adding together multiple single
pulses. The device calculates the distance from the object based on the elapsed time
that the light requires between emitting the beam and receiving the reflection. Radar
systems apply this “pulse time-of-flight measurement” principle in a similar way.
3.6.3
Direction measurement
The device uses a rotating mirror to deflect the emitted laser beams, thereby scanning
its surroundings in a circular pattern. The measurements are triggered internally by an
encoder in regular angle increments.
The measuring procedure uses the averaging from multiple pulses to determine individ‐
ual measured values. A measuring point is the average value of several measurements
combined.
1
2
1
Device
2
Laser pulse
3
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
14
O P E R A T I N G I N S T R U C T I O N S | TiM781
8024231//2019-03-29 | SICK
Subject to change without notice