Publication 1747-UM013B-EN-P - January 2005
A-10
Specifications
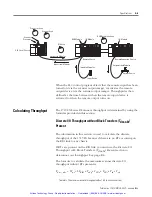
Tdm-bt = 2(25.0) + 2TRIO + 2Tbtx + 9.0 + 22.0 + 5.0 + 10.0 + 1.0
2.
Calculate the total RIO scan time (TRIO). Locate the baud rate
(115.2K) and adapter size which is found in the table on page
B-4. Multiply the RIO scan times listed under the 115.2K heading
by the number of each different type of rack that you have. Add
those number together.
TRIO = Tad Tad Tadapter3
TRIO = 1(5.5) + 1(4.0) + 2(3.5)
TRIO = 16.5 ms
3.
Calculate the maximum Tri time for each logical rack. Do this by
determining the largest BT that will occur to any device within a
logical rack and calculating the transfer time using the table on
page B-7. Then add together the Tri times for each logical rack
to obtain Tbtx.
Tri for rack 0 = 0.150(8) + 3.5 = 4.7 ms (maximum BT to rack 0
is 8 words)
Tri for rack 1 = 0.150(2) + 3.5 = 3.8 ms (maximum BT to rack 1
is 2 words)
Tri for rack 2 = 0.150(64) + 3.5 = 13.1 ms (maximum BT to rack
2 is 64 words)
Tbtx = Tri0 + Tri1 + Tri2 = 4.7 + 3.8 + 13.1 = 21.6 ms
4.
Substitute all the values for variables in the throughput formula
and solve for throughput.
Tdm-bt = 2(25.0) + 2(16.5) + 2(21.6) + 9.0 + 22.0 + 5.0 + 10.0 +
1.0
Tdm-bt = 173.2 ms = maximum throughput
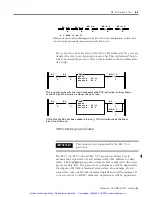
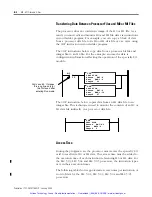
Block Transfer Throughput
Block transfer throughput is the time from when the BT is enabled via
the EN bit, until the DN bit is processed. The following BT timing
explanations are based on the directional continuous BT example
Artisan Technology Group - Quality Instrumentation ... Guaranteed | (888) 88-SOURCE | www.artisantg.com