2200M4JE-HO-iS2-N_2014.04.
Chapter 5 Maintenance and Inspection
Screw Compressor i-series
5.2 Maintenance and Inspection List
5-2
5.2
Maintenance and Inspection List
5.2.1 Daily
Management
As daily management, check the items listed in Table 5-1 "Daily Inspection Items" and record the
results.
By regularly recording the daily operational data in an operation log, it should be able to detect any
significant change in the system. This is significantly effective in preventing compressor failures.
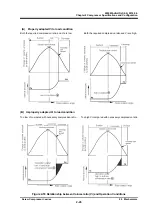
It is particularly important to check whether the temperature/pressure correlations related to the
refrigerant evaporation and condensation is proper. This makes it possible to quickly find out problems
in the compressor or the system.
If a failure or accident should occur in the compressor or the system, the operation logbook will help
determine the cause and take prompt and proper actions.
In addition to the items listed in Table 5-1, it is necessary to record and manage unit components and
load side conditions on a daily basis. For their details, refer to the operation manual of the unit.
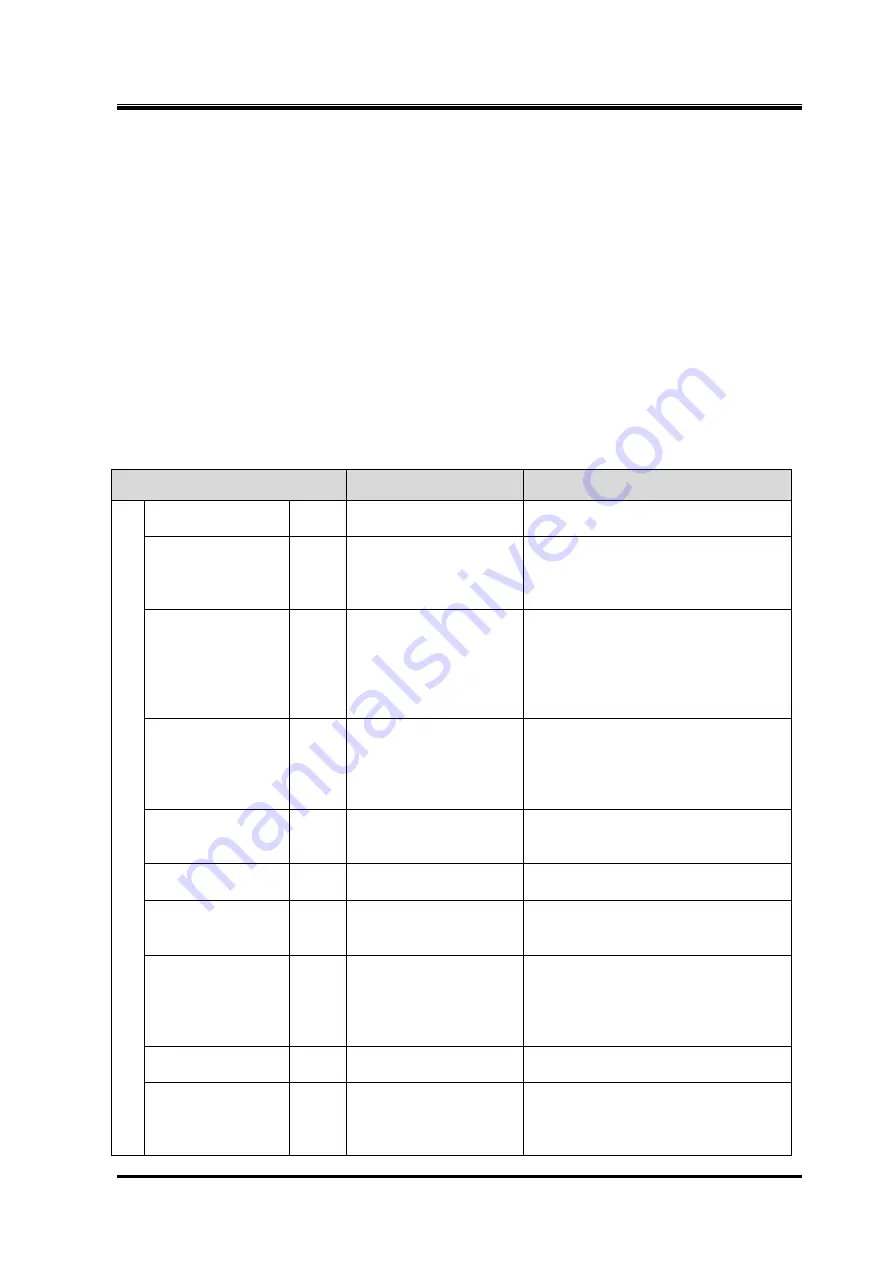
Table 5-1
Daily Inspection Items
Inspection Item
Inspection Details
Check Items/Actions
Comp
re
s
s
or
Operating hours
h
Total operating hours
Judgment of periodic maintenance
interval
Suction pressure
Mpa
Difference from the set
value of evaporation
temperature
equivalent pressure
Contamination on the cooling pipe
surface
Temperature, flow rate, etc. of the
object to be cooled
Discharge
pressure
MPa
Difference from
cooling water
temperature
equivalent condensing
pressure
Contamination on condenser
cooling pipes
Non-condensable gases mixed
into the system
Quantity, temperature, etc. of
cooling water
Oil supply
pressure
MPa
Difference from
discharge pressure
Whether differential pressure is
decreasing
Operation with liquid flow-back
Whether compressor parts are
worn
Oil filter pressure
loss
MPa Pressure
difference
between oil filter inlet
and outlet
Contamination of lubricant
Clogging of oil filter
Suction
temperature
℃
Whether within upper
and lower limits
Temperature, flow rate, etc. of the
object to be cooled
Degree of
superheat for
suction
℃
Whether degree of
superheat is proper
Adjust expansion valve
Insufficient refrigerant flow
Discharge
temperature
℃
Whether within upper
limit
Non-condensable gases mixed
into the system
Oil supply temperature, insufficient
oil supply
Compressor failure
Oil supply
temperature
℃
Whether within upper
and lower limits
Contamination on cooling pipes of
oil cooler
Capacity control
Specified load
%
Whether operation is
normal
Damage to solenoid valve coil
Improper adjustment of manual
control valve of electromagnetic
assembly
Com
p
re
s
s
or