Soft jaw
(Incorrect)
T nut
Body
Body
Hard jaw
T nut
Body
Body
(Correct)
φd
φD
φD
φD'
B
A
Top jaw attaching bolt
Top jaw
T nut
0〜1mm
Reference
Entire stroke
Master jaw
Appropriate stroke
・Use the T nut so that it does not come out from the master jaw. (Refer to Fig.9)
・It if the T nut comes out from the master jaw, the master jaw and T nut will break causing the work to fly out and a
possible precision failure.
・Always tighten the bolts at the specified torque. If the torque is insufficient or excessive, the bolt will break, which
is dangerous as the chuck or work will fly out.
17
18
1.Preparation of the plug for forming
・Prepare the plug for forming. The surface roughness of the plug
outside diameter is to be approximately 25s, and make a shape
with sufficient thickness which does not distort.
・It is convenient to prepare various outside diameter dimensions for
dimensions of forming parts.
・It is convenient to process tapping in the center part of the plug
and to guide with a bolt, etc.
2.Process of the plug gripping part for forming
・Operate the switch valve and maximize the opening of the jaw.
・Then, process the φD part (part to grip the plug for forming). Set
the dimension φD so that gripping near the center of the jaw
maximum stroke (diameter) is possible.
・φD = φd + (jaw maximum stroke/2)
3.Gripping of the plug for forming
・By operating the switch valve, grip the plug for forming in the φD
part. At this time, grip by pressing the plug on the chuck front
surface in order for the plug not to be tilted. Repeat chucking
several times to stabilize the plug.
4.Forming
・Process the gripping part (dimension φD') of the work in the state
that the plug is kept gripped. The φD' part is to be approximately
the same diameter (H7) as the diameter of the gripping part of the
work, and process to be surface roughness at 6s or less.
・Set the hydraulic pressure during forming the same as during
processing of the work, or slightly higher.
・When the plug distorts, lower the hydraulic pressure or change the
plug into a shape which does not easily distort.
5.Trial cutting
・Remove the plug for forming and grip the work to check the jaw
stroke.
・Implement trial cutting to check the process precision and that
there is no slip, etc.
・Contacting on the gripping surface is to be 2 points contact of the
side A and the side B when gripping.
4−1 Attachment of soft jaw
4−2 . Forming soft jaw with outside diameter gripping
Fig.9
4 . Forming Soft Jaw
DANGER
The attaching position of the soft jaw can be adjusted by loosening the socket head cap screw, attaching the soft jaw
and by changing each serration engagement position.
Use the most appropriate soft jaw considering the shape, dimension, material, and surface roughness of the work and
the cutting conditions, etc.
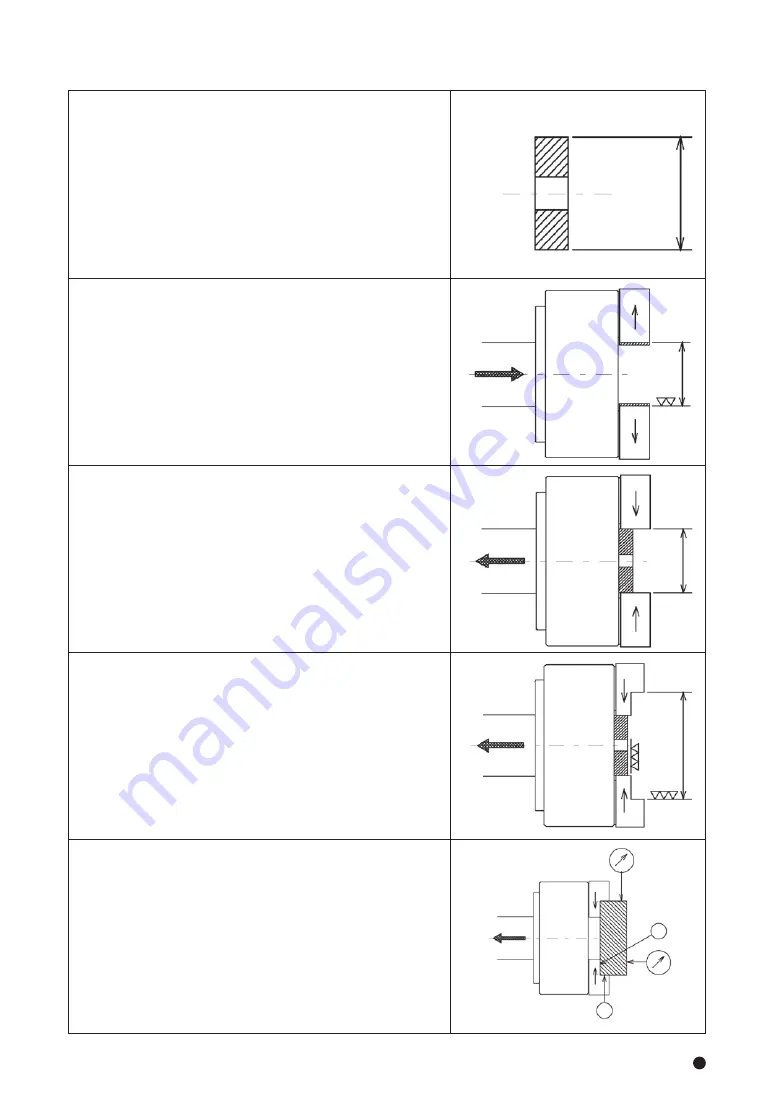
・If the screw-in depth of the jaw attaching bolt to the T nut is shallow, the T nut will
break, and this is dangerous as the jaw and work will fly out. If the attaching bolt is
too long and comes out from the bottom of the T nut as well, this is dangerous as
the jaw and work will fly out since the top jaw is not fixed. Therefore, the overall
length of the jaw attaching bolt must be approximately 0 to -1mm from the bottom
of the T nut (Refer to Fig.10).
・Use the T nut and the attaching bolts attached to the chuck and do not use bolts
other than these. If commercially available bolts are used for an unavoidable
reason, use bolts at the strength classification 12.9 (strength classification 10.9 for
M22 or more) or more, and pay sufficient attention to the length.
・Do not rotate the chuck so that the T nut is loosened causing the jaw to fly out.
・Check that the reference mark on the side of the No. 1 master jaw is within the range of the entire stroke as shown in Fig. 11. Full
stroke the jaw at least once a day to check it before work or when supplying grease, etc. If it goes out of the range of appropriate
stroke due to loosening of the draw nut, etc., the work may not be gripped, and this is dangerous as the work will fly out.
・When gripping the work, use it by keeping the position of the master jaw within the
appropriate stroke range. Gripping in the center of the stroke is the most stable for
the mechanism, and the best precision can be obtained.
・When gripping near the stroke end, the work may not be gripped sometimes
according to the deviation, etc., of the gripping part allowance of the work, and this
is dangerous as the work will fly out.
・ When gripping near the stroke end, the chuck may break and the chuck or work
could fly out.
Fig.10
Fig.11
DANGER
Table 3
Bolt size
Tightening torque
M 5
M 6
M 8
M10
7.5 N・m
13 N・m
33 N・m
73 N・m
Bolt size
Tightening torque
M12
M14
M16
M20
107 N・m
171 N・m
250 N・m
402 N・m
Bolt size
Tightening torque
M22
M24
539 N・m
666 N・m
Appropriate stroke range(mm)
1
2
2.3
3
Type
BB206
BB208
BB210
BB212
Table 4
Содержание BB200 Series
Страница 35: ......
















































