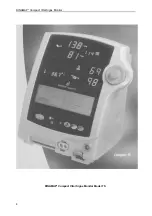
DINAMAP*
Compact
Vital Signs Monitor
17
2.3 Overall Principles of Operation
This section of the manual describes the principles of operation of the DINAMAP
* Compact
monitor.
The section is arranged to give an overall description of the instrument, the following sections then
detail each of the functional systems. For full assembly drawings, circuit diagrams and parts lists of the
component circuit boards, refer to section 8 this manual. The system block diagram of the DINAMAP*
Compact
monitor is shown in drawing 8600EB.
Patient vital signs can be measured by a variety of electronic sensors, including oscillatory pressure
sensors for Non-Invasive Blood Pressure measurement. Both the DINAMAP*
Compact
T and TS
models are provided with a predictive temperature parameter determination. The
Compact
TS model
is also equipped with a Nellcor Puritan Bennett
TM
Blood Oximetry module enabling oxygen saturation
and heart rate to be determined from information received via a finger sensor.
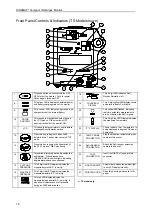
Operator access is via buttons and the rotor located on the front panel. A liquid crystal graphics display
module provides the user with menu, alarm and status information as well as a plethysmograph display
or a record of previous measurements. Parameter information is presented by multiplexed seven
segment LED displays and discrete LED indicators. A thermal printer provides hard copies of patients
vital signs either automatically or on demand. A built-in speaker and piezo-electric sounder advise the
user of pulse signals and alarm conditions.
The monitor is designed to operate from AC mains via the supplied power converter, or from an internal
rechargeable battery. The external AC power converter rectifies the mains to produce a raw DC supply
which is regulated internally to provide the DC operating power. The external raw DC source is
employed to charge the internal batteries. The real time clock and user monitor settings are maintained
by an internal rechargeable NiCd backup battery.
The monitor includes a pneumatics system required for NIBP operation. NIBP determinations are
made by pumping up the air pressure in a restrictive cuff and monitoring the oscillatory signals in the
system as the pressure is released. Large deflation steps are employed for NIBP and the system
processor interpolates measurements between steps. The pneumatic system then regulates operation
of the pneumatic pump and valves. An overpressure sensor provides independent protection against
over-inflation. Protection against deflation failure is inherent in the design; the valve and pneumatic
system being designed to auto-deflate the system in the event of power fail or alarm situations.
Blood Oximetry (SpO
2
) determinations (model TS only) are made using a proprietary module from
Nellcor Puritan Bennett
TM
which communicates the parameter measurements to the system processor
via an internal serial port.
Predictive temperature measurements are made using a thermocouple type sensor. The temperature
sensor signal and two calibration reference points are measured by the system processor. A user
selectable algorithm is applied to produce a value equivalent to either a 3 or 12 minute mercury in glass
reference. The facility to automatically determine oral or rectal sensor type is provided.
2.4 Functional Description
The functions of the DINAMAP*
Compact
monitor can be separated into eleven discrete parts. The
following paragraphs describe each of the Monitor, with full circuit diagrams provided in section 8.
2.4.1 System Processor
The system processor is based on 68302 microprocessor IC22 on the Main Board 8610AB. A master
19.6608 MHz clock generated by XL1 exits the system processor at pin 98 and is divided by 16 inside
binary ripple counter IC36 to provide the 1.23 MHz ADC clock. Communication between
microprocessor IC22 and all bus devices is provided by a 24-bit address bus, 8-bits data bus and the
three wire serial peripheral interface (SPI) bus. The system processor is equipped with a watchdog
timer and reset circuit.