14
STV50 ed 09/08
VICTRIX 50 Rev. 002
10
8
4
12
9
1
11
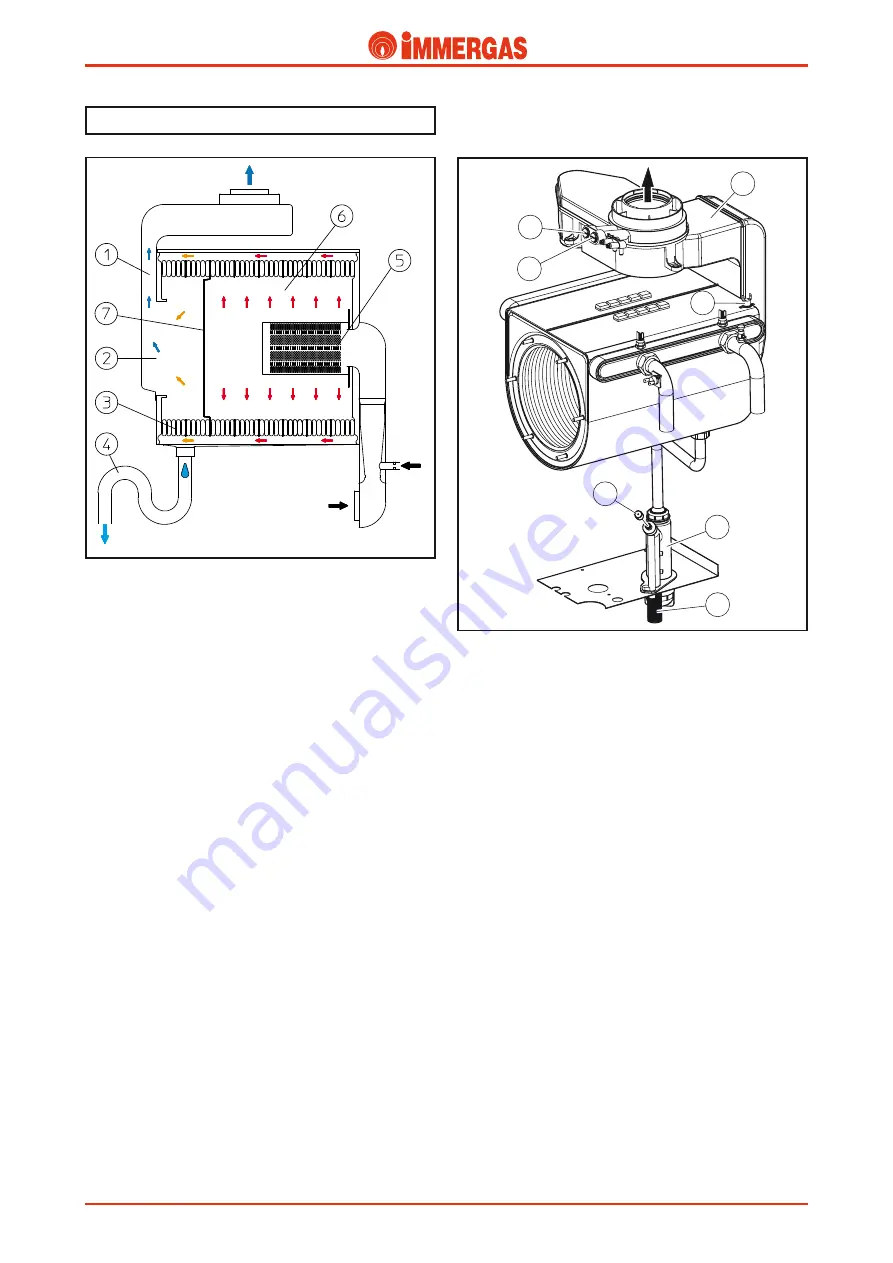
Condensate drain trap (4).
Collects the condensate that forms during boiler functioning
from the bottom of the module.
Its outlet is connected to the draining pipe (11) towards which
the passage of water is allowed but not the passage of fumes,
which could occur following obstruction of the evacuation
pipes.
The height of the column of water in the siphon is in fact
greater than the pressure detected inside the sealed chamber
(module)
with the fan at maximum speed and the evacuation
pipes blocked at functioning limits.
This, however, prevents the draining of combustion products
into the sewers.
On commissioning fumes may escape from the exhaust pipe
(11) which disappear after a few minutes of functioning when
the condensate has reached a sufficient height. If this should
take too long, fill the siphon with water after having removed
the cap (10), which must be re-positioned correctly at the end
of the operation.
Air-flue sample points (8-9).
There are two sample points in the upper part of the boiler
with screw fastening, with front access, after having removed
the plastic cover and from where the combustion agent air (8)
and combustion products (9) can be withdrawn.
Flue circuit.
Operating.
The functioning of the fan positioned at the entry of the air-
gas mixing pipe, guarantees the fan-assisted expulsion of the
fumes produced by the cylindrical burner (5).
These directly hit the first eight elements of the primary heat
exchanger inserted in the sealed combustion chamber (6) which
has a sheet steel section on its base (7) that divides it from the
condensation chamber (2) and diverts the flow of fumes to the
outside of the module.
In this way the flue gases, before entering the condensation
chamber (2), hit the last three elements (3) of the heat exchan-
ger, inside which primary circuit return water runs.
This cools the combustion products further and makes their
condensation easier before escape from the flue hood (1).
The water condensate formed inside the heat exchanger, in
the flue hood and also in the evacuation pipes flows into the
lower part of the module from where, before being discharged,
is conveyed into a trap (4).
Flue hood (1).
It is connected to the rear part of the condensation module
and conveys the combustion products towards the drain fitting
present in the upper part of the appliance.
It is affected by the passage of fumes and water condensate
formed inside it or in the exhaust pipes.
It is constructed in plastic, resistant to the corrosive effects of
the condensate and can work to a temperature of 130 °C
(max.
flue temp with flow 85° C = 78° C)
.
A flue safety thermostat is inserted onto the condensation
module (12), to protect the flue hood (1) and which intervenes
when the temperature detected on the condensation module
exceeds110° C.
Gas
Air
Condensate drain
Flue exhaust
Technical Documentation
Technical Documentation















































