32
INS
TALLER
US
ER
MAINTEN
AN
CE TECHNI
CI
AN
3.3 TROUBLESHOOTING.
N.B.:
maintenance operations must be carried
out by an authorised company (e.g. Authorised
After-Sales Technical Assistance Service).
- Smell of gas. Caused by leakage from gas circuit
pipelines. Check sealing efficiency of gas intake
circuit.
- Repeated ignition blocks. No gas, check the
presence of pressure in the network and that
the gas adduction cock is open. Incorrect
adjustment of the gas cock, check the correct
calibration of the gas valve.
- Irregular combustion or noisiness. It may be
caused by: a dirty burner, incorrect combustion
parameters, intake-exhaust terminal not cor-
rectly installed. Clean the above components
and ensure correct installation of the terminal,
check correct setting of the gas valve (Off-Set
setting) and correct percentage of CO
2
in flue
gas.
- Frequent interventions of the overheating
safety thermostat. It can depend on the lack
of water in the boiler, little water circulation
in the system or blocked pump. Check on the
manometer that the system pressure is within
established limits. Check that the radiator
valves are not closed and also the functionality
of the pump.
- Drain trap clogged. This may be caused by
dirt or combustion products deposited inside.
Check, by means of the condensate drain cap,
that there are no residues of material blocking
the flow of condensate.
- Heat exchanger clogged. This may be caused
by the drain trap being blocked. Check, by
means of the condensate drain cap, that there
are no residues of material blocking the flow of
condensate.
- Noise due to air in the system. Check opening
of the special air bleeding cap. Make sure the
system pressure and expansion vessel pre-
charge values are within the set limits; The
factory-set pressure values of the expansion
vessel must be 1.0 bar, the value of system
pressure must be between 1 and 1.2 bar. Check
that system filling and air bleeding has been
performed according to the requirements.
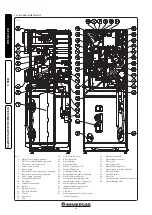
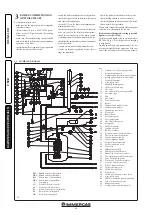
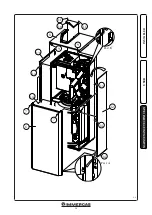
- Noise due to air inside the condensation
module. Use the manual air vent valve (Part.
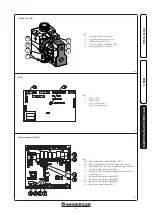
31 Fig. 1-28) to eliminate any air present in the
condensation module. When the operation has
been performed, close the manual vent valve.
- Domestic hot water probe faulty. In order to
replace the DHW probe, the storage tank does
not have to be emptied as the probe is not in
direct contact with the DHW inside the storage
tank.
3.4 CONVERTING THE BOILER
TO OTHER TYPES OF GAS.
If the boiler has to be converted to a different
gas type to that specified on the data nameplate,
request the relative conversion kit for quick and
easy conversion.
The gas conversion operation must be carried
out by an authorised company (e.g. Authorised
After-Sales Technical Assistance Service).
To convert to another type of gas the following
operations are required:
- disconnect the appliance;
- replace the nozzle located between the gas pipe
and gas/air mixing sleeve (Part. 16 Fig. 1-28),
taking care to disconnect the appliance during
this operation;
- re-power the appliance;
- calibrate the number of fan revolutions (parag.
3.5):
- adjust the correct air/gas ratio (parag. 3.6);
- seal the gas flow rate regulation devices (if set-
tings are modified);
- after completing the conversion, apply the
sticker, contained in the conversion kit, near the
data nameplate. Using an indelible marker pen,
delete the data relative to the old type of gas.
These adjustments must be made with reference
to the type of gas used, following that given in
the table (Par. 3.19).
3.5 CALIBRATION OF NUMBER OF FAN
REVS.
Attention:
Verification and calibration is neces-
sary, in the case of transformation to other types
of gas, in the extraordinary maintenance phase
with replacement of the PCB air/gas circuit com-
ponents or in the case of installations with fume
extraction systems, with horizontal concentric
pipe measuring more than 1 metre.
The boiler heat output is correlated to the length of
the air intake and flue exhaust pipes. This decreases
with the increase of pipe length. The boiler leaves
the factory adjusted for minimum pipe length
(1m). It is therefore necessary, especially in the
case of maximum pipe extension, to check the ∆p
gas values after at least 5 minutes of the burner
operating at nominal heat output, when the tem-
peratures of the intake air and exhaust flue gas have
stabilised. Adjust the nominal and minimum heat
output in the domestic hot water and central heat-
ing modes according to the values in the table (Par.
3.19) using the differential manometers connected
to the ∆p gas pressure points (29 and 30 Fig. 1-28).
Access the configurations menu under the “SER-
VICE” item and adjust the following parameters
(Par. 3.8):
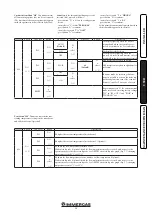
- boiler maximum heat output “P62”;
- boiler minimum heat output “P63”;
- maximum central heating output “P64”;
- minimum central heating output “P65”;
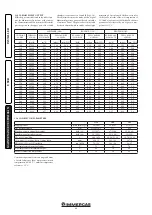
Listed below are the default settings featured
on the boiler:
P62
G20:
4700 (rpm)
LPG:
4700 (rpm)
P63
G20:
1380 (rpm)
LPG:
1380 (rpm)
P64
G20:
4700 (rpm)
LPG:
4700 (rpm)
P65
G20:
1380 (rpm)
LPG:
1380 (rpm)
3.6 ADJUSTMENT OF THE AIR-GAS
RATIO.
Calibration of the minimum CO
2
(minimum
central heating power).
Enter the chimney sweep phase without with-
drawing domestic hot water and take the se-
lector switches to minimum (turn them in an
anti-clockwise direction until "0" is seen on the
display). To have an exact value of CO
2
in the flue
gas the technician must insert the sampling probe
to the bottom of the sample point, then check
that the CO
2
value is that specified in the table,
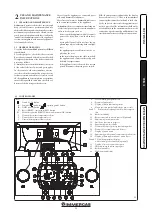
otherwise adjust the screw (3 Fig. 3-3) (Off-Set
adjuster). To increase the CO
2
value, turn the
adjustment screw (3) in a clockwise direction
and vice versa to decrease it.
Calibration of the maximum CO
2
(nominal
central heating power).
On completion of the adjustment of the mini-
mum CO
2
keeping the chimney sweep function
active, take the heating selector switch to maxi-
mum (turn it in a clockwise direction until “99”
is seen on the display). To have an exact value of
CO
2
in the flue gas the technician must insert
the sampling probe to the bottom of the sample
point, then check that the CO
2
value is that speci-
fied in the table, otherwise adjust the screw (12
Fig. 3-3) (gas flow rate regulator).
To increase the CO
2
value, turn the adjustment
screw (12) in an anti-clockwise direction and vice
versa to decrease it.
At every adjustment variation on the screw 12 it
is necessary to wait for the boiler to stabilise itself
at the value set (about 30 sec.).
CO
2
at nominal
output
CO
2
at minimum
output
G 20
9,60% ± 0,5
8,70% ± 0,5
G 30
12,10% ± 0,5
11,30% ± 0,5
G 31
10,70% ± 0,5
10,00% ± 0,5
3.7 CHECKS FOLLOWING
CONVERSION TO ANOTHER TYPE
OF GAS.
After making sure that conversion was carried
out with a nozzle of suitable diameter for the
type of gas used and the settings are made at the
correct pressure, check that the burner flame is
not too high or low and is stable (does not detach
from burner);
Note:
all boiler adjustment operations must be
carried out by a qualified company (e.g. Author-
ised After-Sales Assistance).