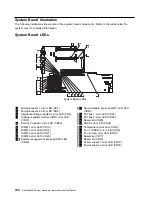
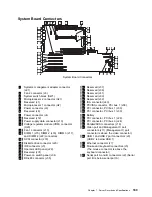
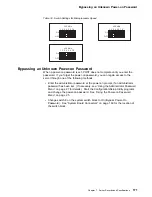
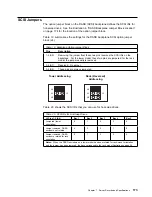
client. A functional unit that receives shared services
from a server. (T)
clock. A device that generates periodic, accurately
spaced signals used for purposes such as timing,
regulation of the operations of a processor, or
generation of interrupts. (T)
code. A collection of instructions that is in a form that
can be read and processed by a computer.
collision. An unwanted condition that results from
concurrent transmissions on a channel. (T)
compatibility. The capability of a hardware or
software component to conform to the interface
requirements of a given computer without adversely
affecting its functions.
configuration. The manner in which the hardware and
software of an information processing system are
organized and interconnected. (T)
configure. To set up a computer for operation by
describing to the system the devices, optional features,
and programs installed in the computer.
connector. An electrical part used to join two or more
other electrical parts. (Contrast with port.)
control. The determination of the time and order in
which the parts of a computer and the devices that
contain those parts perform the input, processing,
storage, and output functions.
controller. A device that coordinates and controls the
operation of one or more input/output devices, such as
workstations, and synchronizes the operation of such
devices with the operation of the system as a whole.
crossover cable. A type of 10BASE-T cable in which
the transmit and receive data pairs are wired so that the
transmit pair is terminated at the pin positions used by
the receive pair at the opposite end of the cable. A
crossover cable is used to connect the 10BASE-T port
on an Ethernet controller to a 10BASE-T port on a
repeater that does not perform the crossover function.
D
DASD. Direct access storage device.
data. (1) A re-interpretable representation of
information in a formalized manner suitable for
communication, interpretation, or processing.
Operations can be performed upon data by humans or
by automatic means. (T) (2) Any representations such
as characters or analog quantities to which meaning is
or might be assigned. (A)
device. A mechanical, electrical, or electronic piece of
equipment designed to serve a special purpose or
perform a special function.
device driver. A file that contains the code needed to
use an attached device.
diagnostic. Pertaining to the detection and isolation of
errors in programs and faults in equipment.
digital. (1) Pertaining to data in the form of digits. (A)
(2) Contrast with analog.
DIMM. Dual inline memory module.
direct access storage device (DASD). A
nonvolatile-storage device, such as a diskette drive,
hard disk drive, or CD-ROM drive, in which access time
is effectively independent of the location of the data on
the storage medium.
direct memory access (DMA). The transfer of data
between memory and input/output devices without
microprocessor intervention.
disk array. Two or more hard disks interconnected to
increase security, performance, or reliability.
diskette. A small magnetic disk enclosed in a jacket.
(T)
diskette drive. The mechanism used to seek, read,
and write data on diskettes. It can be installed in, or
attached to, a computer.
display. A component capable of displaying
information on a viewing surface; for example, a
cathode ray tube or a gas panel.
DMA. Direct memory access.
duplex. Pertaining to communication in which data can
be sent and received at the same time. Synonymous
with full-duplex (FDX).. Contrast with half-duplex
(HDX).
E
ECC. Error correcting code.
ECP. Extended Capability Port. An IEEE 1284
standard signalling method for high speed bidirectional
parallel communication between a computer and a
peripheral device, that uses the hardware in the port to
assist in the data transfer. It can use direct memory
addressing (DMA) channels to move its data, and
requires the peripheral device to control the
handshaking. ECP is generally used for printers and
scanners. See also EPP.
178
Netfinity 5000 Server Hardware Information and Procedures