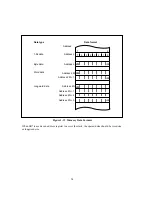
Bit 5—Half-Carry Flag (H): When the ADD.B, ADDX.B, SUB.B, SUBX.B, CMP.B, or NEG.B
instruction is executed, this flag is set to 1 if there is a carry or borrow at bit 3, and cleared to 0
otherwise. When the ADD.W, SUB.W, CMP.W, or NEG.W instruction is executed, the H flag is
set to 1 if there is a carry or borrow at bit 11, and cleared to 0 otherwise. When the ADD.L,
SUB.L, CMP.L, or NEG.L instruction is executed, the H flag is set to 1 if there is a carry or
borrow at bit 27, and cleared to 0 otherwise.
Bit 4—User Bit (U): Can be written and read by software using the LDC, STC, ANDC, ORC,
and XORC instructions.
Bit 3—Negative Flag (N): Indicates the most significant bit (sign bit) of the result of an
instruction.
Bit 2—Zero Flag (Z): Set to 1 to indicate a zero result, and cleared to 0 to indicate a non-zero
result.
Bit 1—Overflow Flag (V): Set to 1 when an arithmetic overflow occurs, and cleared to 0 at other
times.
Bit 0—Carry Flag (C): Set to 1 when a carry occurs, and cleared to 0 otherwise. Used by:
•
Add instructions, to indicate a carry
•
Subtract instructions, to indicate a borrow
•
Shift and rotate instructions, to store the value shifted out of the end bit
The carry flag is also used as a bit accumulator by bit manipulation instructions. Some
instructions leave some or all of the flag bits unchanged. For the action of each instruction on the
flag bits, refer to the detailed descriptions of the instructions starting in section 2.2.1.
Operations can be performed on the CCR bits by the LDC, STC, ANDC, ORC, and XORC
instructions. The N, Z, V, and C flags are used as branching conditions for conditional branch
(Bcc) instructions.
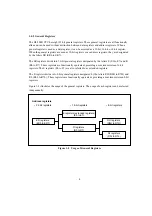
1.4.4 Initial Register Values
When the CPU is reset, the program counter (PC) is loaded from the vector table and the I bit in
the condition-code register (CCR) is set to 1. The other CCR bits and the general registers and
extended registers are not initialized. In particular, the stack pointer (extended register E7 and
general register R7) is not initialized. The stack pointer must therefore be initialized by an MOV.L
instruction executed immediately after a reset.
11