6-86
6
FTP Configuration
This chapter includes these sections:
z
z
z
z
Displaying and Maintaining FTP
FTP Overview
Introduction to FTP
The File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is an application layer protocol for sharing files between server and
client over a TCP/IP network.
FTP uses TCP ports 20 and 21 for file transfer. Port 20 is used to transmit data, and port 21 to transmit
control commands. See RFC 959 for details of FTP basic operation.
FTP transfers files in two modes:
z
Binary mode: Transfers files as raw data, like
.bin
, and
.btm
files.
z
ASCII mode: Transfers files as text, like
.txt
,
.bat
, and
.cfg
files.
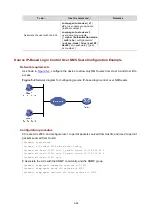
Operation of FTP
FTP adopts the client/server model. Your device can function either as the client or the server (as shown
in
).
z
When the device serves as the FTP client, use Telnet or an emulation program to log in to the
device from the PC, execute the
ftp
command to establish a connection from the device (FTP client)
to the PC (FTP server), and then upload/download files to/from the server.
z
When the device serves as the FTP server, run the FTP client program on the PC to establish a
connection to the FTP server and upload/download files to/from the server.
Figure 6-1
Network diagram for FTP
When the device serves as the FTP client, you need to perform the following configuration: