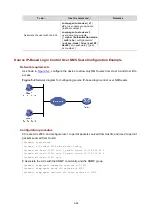
6-95
The boot file used for the next startup must be saved under the root directory of the storage medium
(For a device that has been partitioned, the boot file must be saved on the first partition). You can copy
or move a file to the root directory of the storage medium. For the details of the
boot-loader
command,
see
Software Upgrade
in the
Fundamentals Command Reference
.
Configuring the FTP Server
Configuring FTP Server Operating Parameters
The FTP server uses one of the two modes to update a file when you upload the file (use the
put
command) to the FTP server:
z
In fast mode, the FTP server starts writing data to the storage medium after a file is transferred to
the memory. This prevents the existing file on the FTP server from being corrupted in the event that
anomaly, power failure for example, occurs during a file transfer.
z
In normal mode, the FTP server writes data to the storage medium while receiving data. This
means that any anomaly, power failure for example, during file transfer might result in file
corruption on the FTP server. This mode, however, consumes less memory space than the fast
mode.
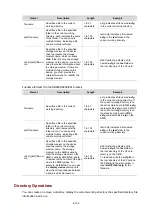
Follow these steps to configure the FTP server:
To do…
Use the command…
Remarks
Enter system view
system-view
—
Enable the FTP server
ftp server enable
Required
Disabled by default.
Use an ACL to control FTP clients’
access to the device
ftp server acl
acl-number
Optional
By default, no ACL is used to control
FTP clients’ access to the device.
Configure the idle-timeout timer
ftp
timeout minutes
Optional
30 minutes by default.
Within the idle-timeout time, if there is
no information interaction between
the FTP server and client, the
connection between them is
terminated.
Set the file update mode for the
FTP server
ftp update
{
fast
|
normal
}
Optional
Normal update is used by default.
Quit to user view
quit
—
Manually release the FTP
connection established with the
specified username
free ftp user username
Optional
Available in user view