6 Installation
6
22
Rittal Liquid Cooling Package
2. Pipework should be protected from the thermal in-
fluence of hot lines and heat sources by means of
spatial separation.
3. Soldering, welding and mechanical joints in connec-
tion pipes (e.g. in split systems) should be carried
out before the fittings are opened, so as to ensure
the flow of refrigerant between the plant parts. A
valve should be provided to extract air from the con-
nection pipes and/or any part of the cooling system
that remains unfilled.
4. Refrigerant lines must be protected or covered to
prevent damage.
5. Flexible connecting parts such as connection lines
between indoor and outdoor devices that could be-
come displaced during regular work operations
must be protected against mechanical damage.
6. The maximum distance between the brackets of the
copper pipes is 2 m.
Laying the pipework
1. The equivalent length of the overall line between the
LCP DX and the condenser must not exceed a max-
imum of 45 m. To calculate the equivalent length, in
addition to the actual length of the pipeline, the
equivalent length of curves and valves should be
taken into account.
2. The number of curves should be kept to a bare min-
imum so as to avoid pressure losses. Where curves
are unavoidable, the radius chosen should be as
large as possible.
3. When planning the piping layout ensure that the
lines between the LCP DX and the condenser are as
short as possible. Only allow for exceptions to save
unnecessary bends.
4. If at all possible, do not conduct refrigerant lines
through rooms which are ouccpied by people, such
as offices and meeting rooms.
5. The gas line must be laid with an incline of 1% in the
direction of flow of the coolant.
6. A distance of at least 20 mm between the gas and
the liquid line should be observed. If this is not pos-
sible, both lines should be adequately insulated.
7. When laying out the refrigerant lines, be sure no sag
is created in which oil may collect; install oil traps if
necessary.
8. Provide one elevation arc at least every 6 m of line
length.
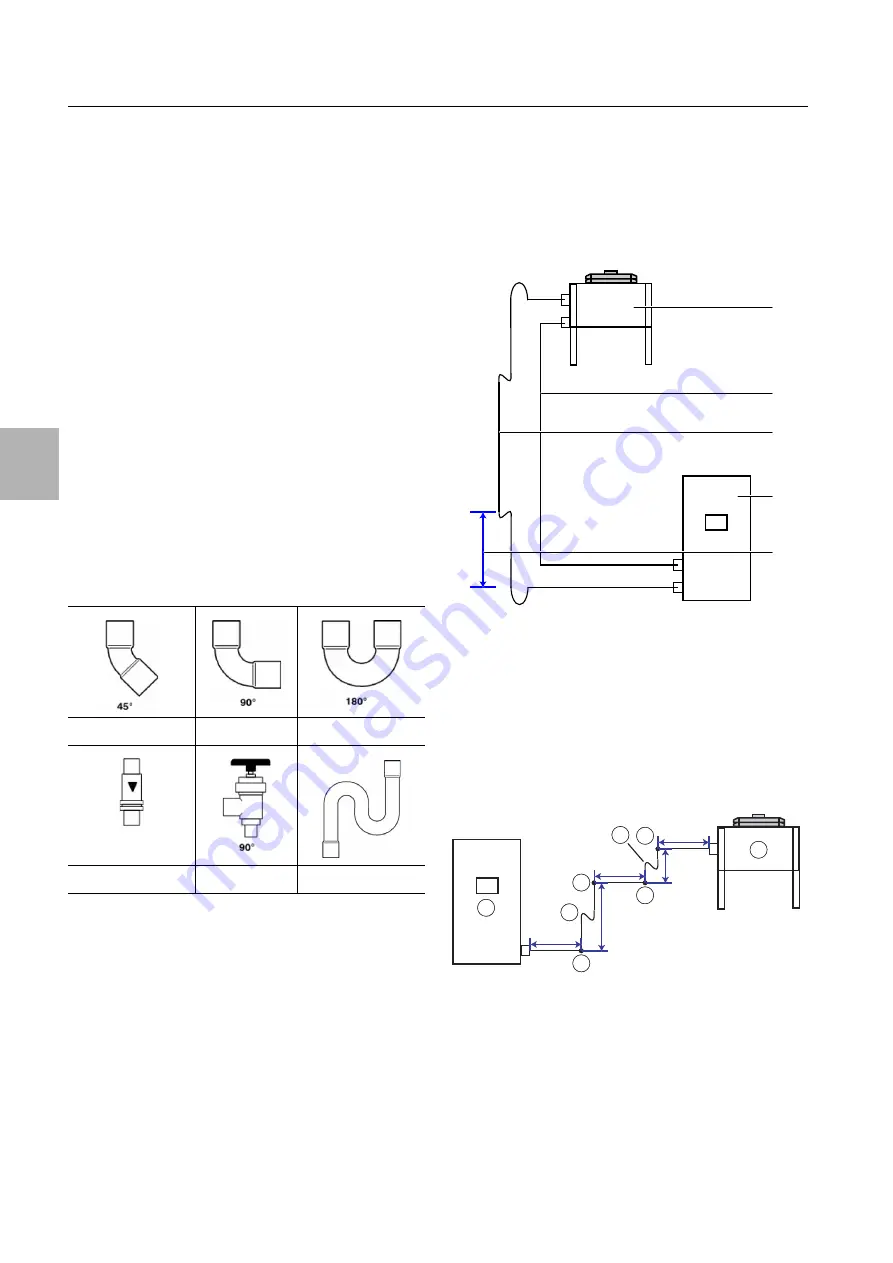
Fig. 21:
Oil elevation arc
Key
1
External condenser
2
Liquid line
3
Hot gas line
4
LCP DX
5
Spacing max. 6 m
Sample calculation of overall length
Calculating the overall length of the pipeline is explained
using the following diagram.
Fig. 22:
Simplified representation of connection lines
Key
1
Curves 90° (4 x)
2
Oil elevation arc (2 x)
3
External condenser
4
LCP DX
The
overall length
of the pipeline is comprised of the
actual
length of the pipeline and the
equivalent
length
of the installed moulded parts. The equivalent length
makes allowance for pressure loss from moulded parts
0.25 m
0.5 m
0.75 m
1.90 m
2.10 m
3.0 m
Tab. 5:
Equivalent length for external diameter 12 mm
2
1
3
4
5
1
1
1
2
1
2
1
1
1
4
1
3
1
1
1
1
4 m
3 m
3 m
3 m
2 m















































