4 Fluidmesh Architecture
Overview
4.1
Point-to-Point Wireless Bridge (FM1100 only)
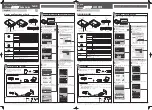
A wireless bridge enables two local networks (i.e., network segments) to
communicate with each other. A sample network architecture which in-
cludes the FM1100 operating as a wireless bridge is depicted in Fig. 4.1.
The wireless bridge is defined as “transparent” because its activity is trans-
parent to the network hosts. In other words, the wireless bridge forwards
packets from one network segment to the other according to a “forwarding
table” which is built by learning the network topology from the analysis of
the incoming traffic. In this configuration, no explicit interaction between
the wireless bridge and the network hosts takes place. The two network
segments, connected to both sides of the wireless bridge, will share the
same IP addressing class. Thus, each network host must use a unique
IP address, i.e., it is not allowed to have two devices sharing the same IP
address.
4.1.1
Bridge IP Addressing
Each FM1100 is provided with a default IP address for its wired Ethernet
port, which is:
192.168.0.10
No IP address is associated to the wireless interface.
When you set up a wireless bridge using two FM1100 units for the first time,
both units will have the same default IP address equal to 192.168.0.10.
It is recommended to change the IP address of one of the two units in
order to univocally address and configure the system with no confusion
(see Fig. 4.1).
15