22
C6.2.38/0719/E
to chemical reactions of the oil with the refrigerant and the compounds extracted from sealants
and insulation material. As a consequence contaminants of various types, among them acids, will
form inside the system.
4.7.2 Compressor discharge gas temperature protection
Under some extreme operating conditions (such as loss of charge or improper control operation),
the internal discharge gas temperature reached can cause compressor damage. To guarantee
positive compressor protection, discharge gas temperature protection is required for any application
with Copeland brand compressors. This protection must not be used as an operating envelope
controller but as a safety device.
YBVH* compressors do not have an internal discharge temperature protection. Emerson offers NTC-
discharge temperature sensors for the installation on the discharge piping of the compressor, to be
connected electrically to the ED3 inverter
– see the Emerson User Manual for ED3 for correct
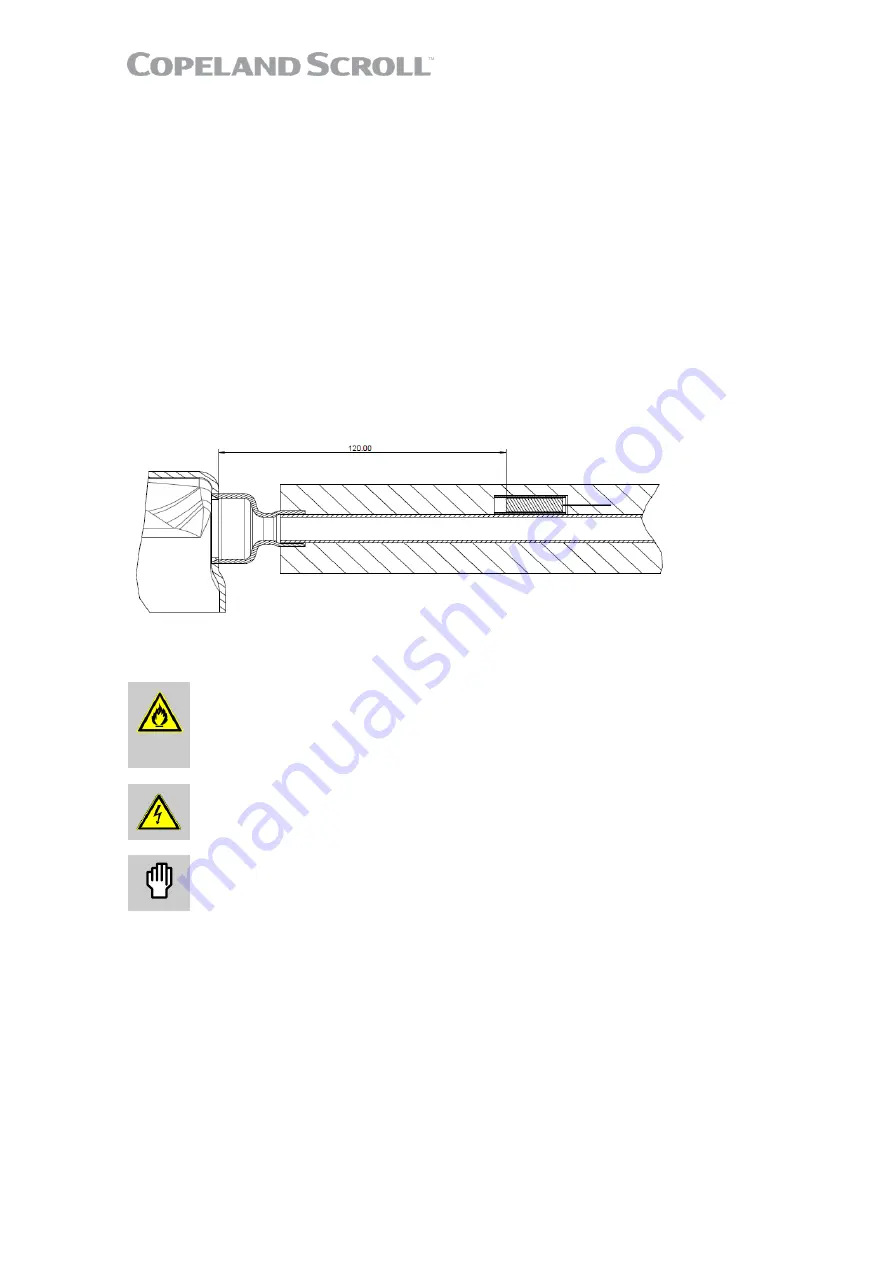
connection and further details. The NTC-sensor must be attached to the compressor discharge line
less than 12 cm from the compressor discharge fitting. For best response the sensor must be
insulated and placed in a sleeve braced on the discharge pipe
– see
Figure 19
. If you use thermal
compound to improve the heat transfer from sleeve to sensor, make sure it is approved for these
temperatures. Also protect the sensor from being removed from its position by transport; vibration or
any other incident. Refer to the operating map for maximum operating discharge line temperatures.
Figure 19: Discharge temperature sensor mounting
4.8 High-potential testing
WARNING
High potential testing in a flammable atmosphere! Fire hazard!
Make sure
the atmosphere is non-flammable before performing high potential testing. Do
not perform any high potential test when the compressor is charged with
flammable refrigerant.
WARNING
Conductor cables! Electrical shock!
Shut off power supply before high-
potential testing.
CAUTION
Internal arcing! Motor destruction!
Do not carry out high-voltage or
insulation tests if the compressor housing is under vacuum.
Emerson subjects all scroll compressors to a high-voltage test after final assembly. Each motor
phase winding is tested according to EN 60034-1 at a differential voltage of 1000V plus twice the
nominal voltage.
Since high-voltage tests lead to premature ageing of the winding insulation, further additional tests
of that nature are not recommended. However, if it has to be done for any reason, it shall not be
made with the compressor charged with refrigerant. Carry out the test with a lower voltage, as
described above. Disconnect all electronic devices, eg, motor protection module, fan speed control,
etc prior to testing.
Special attention should be paid when performing a high-potential test and reading the Megaohm
resistance on an R290 compressor as these tests can induce an electrical arc and cause a potential
fire/explosion hazard.
For the same reason, compressors removed from an R290 system will need to have the oil drained
and a nitrogen purge introduced to flush any remaining refrigerant from the compressor prior to high-
potential testing and Megaohm resistance reading.